
在本 C 教程中,您将精通所有关于决策语句的内容,例如 if、if-else、if-else if、嵌套 if 等。此外,您还将学习如何通过示例在 C 语言中使用 switch 和嵌套 if。
程序中几乎所有涉及逻辑运算的算法都必须经过决策架构。计算机的算术逻辑单元(ALU)通过 AND、OR、NOT、NAND 等逻辑门来监督决策语句的执行。最简单的决策语句形式是“如果发现某事,则做这个,否则做那个”。在接下来的部分,我们将学习如何在 C 语言中使用它。
'if' 是一个重要的关键字,它告诉编译器查找某些条件或标准。如果数据满足给定条件,则会执行特定的代码块。如果提供的标准不匹配,它会将执行控制切换到另一个预定的代码块。
if (condition)
{
#body of if ;
}
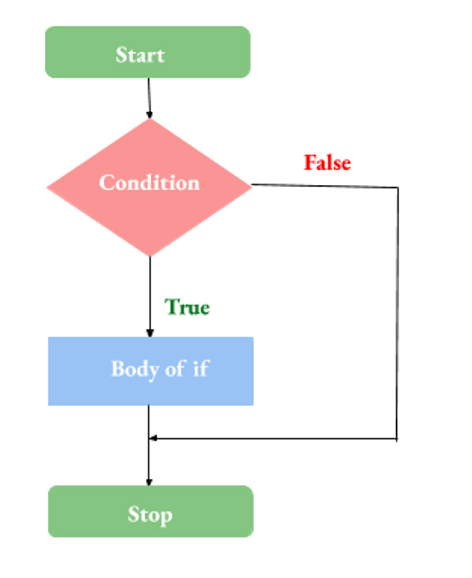
假设,如果用户输入的数字是“0”,您想打印“它是零”。代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int num;
printf("Enter a number:");
scanf("%d",&num);
if(num==0)
{
printf("Entered Number is zero\n");
}
printf("Exit");
}
输出
Enter a number:0 Entered Number is zero Exit
Enter a number:2 Exit
因此,您一定注意到条件写在 'if' 后面,用括号 () 括起来,而条件满足时要执行的代码块写在花括号 {} 中。
单个 if 语句的缺点是它只执行真值之后的语句,不处理真和假两种情况。
'else' 是另一个有用的关键字,仅与 'if' 关键字一起使用。当编译器找到 'else' 时,它只会在条件不满足时执行其后的代码块。原型:
if (condition)
{
#body of if ;
}
else
{
#body of else ;
}
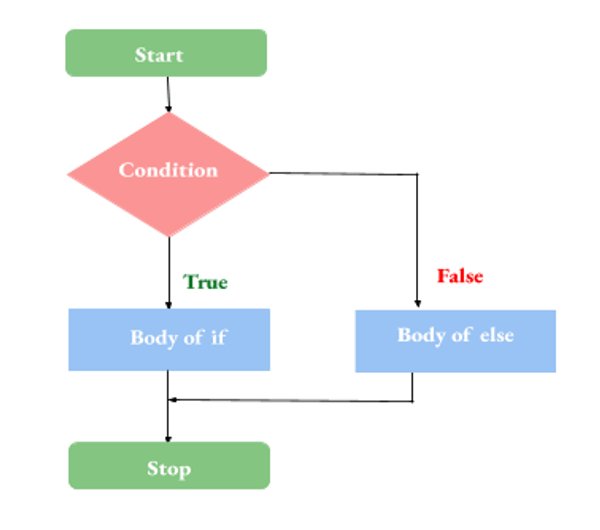
下面是一个演示 If..else 原型用法的简单程序。
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int num;
printf("Enter a number:");
scanf("%d",#);
if(num==0)
{
printf("Entered Number is zero\n");
}
else
{
printf("Entered Number is not zero\n");
}
printf("Exit");
}
Output 1: Enter a number:0 Entered Number is zero Exit Output 2: Enter a number:2 Entered Number is zero Exit
到目前为止,我们处理了两个独立的代码块。但很多时候,您会遇到需要多个代码集,并且需要根据数据输入来执行它们的情况。
if (condition 1)
{
#body of if ;
}
else if(condition 2)
{
#body of elseif ;
}
else
{
#body of else ;
}
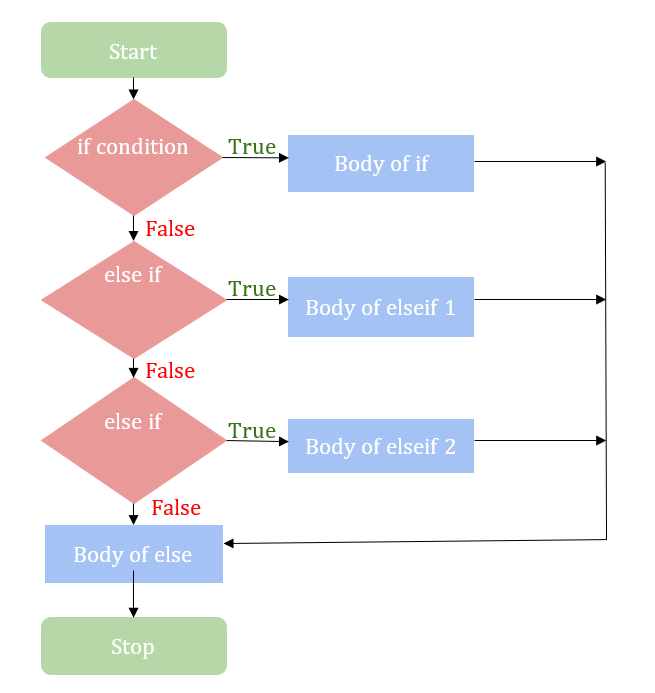
假设我们正在比较两个数字 a 和 b。如果我们想比较它们,会出现三种不同的情况:a>b、a=b 和 a 除了使用 if-else 结构,我们还可以在另一个 if 的块中使用 if-else 语句。对于长而复杂的程序,程序员总是倾向于使用这种架构。 上面的程序已使用“嵌套 if”重写 在上面的代码片段中,最初会评估非相等条件。如果评估为真,则控制会转移到嵌套的 if 语句,在那里它会比较两个值中较大的那个,否则它将执行 else 部分。 顾名思义,它负责将执行流程切换到所需的代码部分。对于每个不同的“case”,代码都应该单独编写,然后跟一个 'break' 语句,将控制权交给下一层代码。如果您想在任何定义的 'case' 都不匹配时运行另一个代码块,可以在 'default' 下编写。 请查看以下程序 在此程序中,如果您输入 0 到 7 之间的任何数字,'default' 下的代码将执行,显示“无效日期”。 嵌套 switch 语句与嵌套 if 语句是对称的。它允许程序员在单个 case 下定义两个或多个独立的 case。其语法如下: 符号“?”在 C 语言中用作布尔运算符,将 if-else 语句合并为一行。它有三个操作数。这里可以使用“?”编写一个奇偶程序。 您可以轻松理解,单行 a= ((n%2==0)? 1:0) 意味着: if (n%2==0) a=1; else a=0; 因此,使用条件运算符 ? 可以大大减少代码量,并使您的程序看起来更紧凑。#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b;
printf("Enter first number: ");
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("Enter second number: ");
scanf("%d",&b);
if(a>b)
{
printf("\n%d is greater than %d",a,b);
}
else if(a<b)
{
printf("\n%d is less than %d",a,b);
}
else
{
printf("\nTwo numbers are equal");
}
}
<stdio.h>
Output 1:
Enter the first number 8
Enter the second number 5
8 is greater than 5
Output 1:
Enter the first number 5
Enter the second number 8
5 is less than 8
Output 2:
Enter the first number 5
Enter the second number 5
Two numbers are equal
嵌套 if
嵌套 if 的语法
if (condition)
{
#body of if ;
}
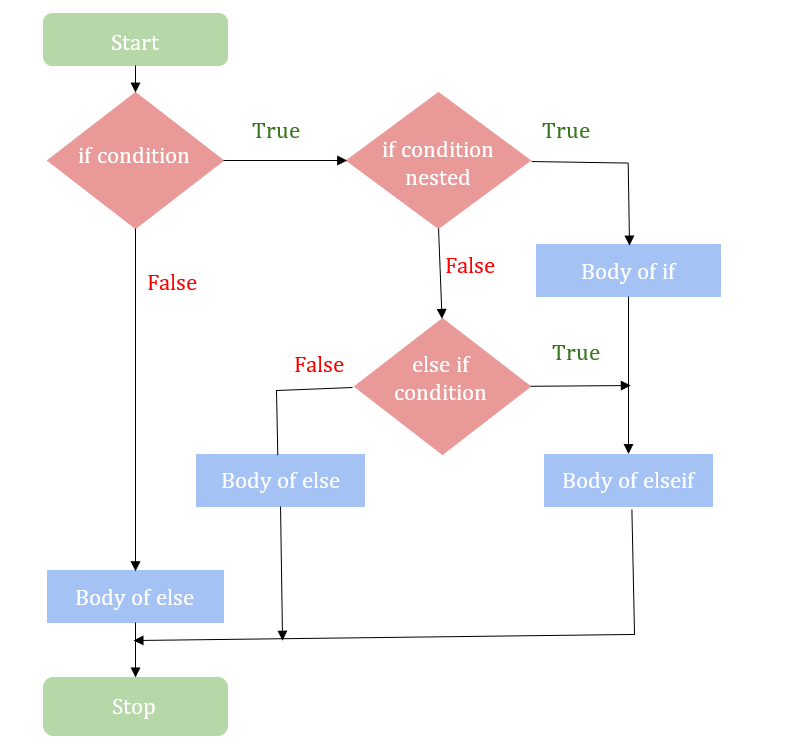
嵌套 IF 语句流程图
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b;
printf("Enter first number: ");
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("Enter second number: ");
scanf("%d",&b);
if(a!=b)
{
if(a>b)
printf("\n%d is greater than %d",a,b);
else
printf("\n%d is less than %d",a,b);
}
else
printf("\nTwo numbers are equal");
}
Output 1:
Enter the first number 8
Enter the second number 5
8 is greater than 5
Output 2:
Enter the first number 5
Enter the second number 8
5 is less than 8
Output 3:
Enter the first number 5
Enter the second number 5
Two numbers are equal
C 中的 switch 语句
C 中 switch 语句的语法
switch(Expression)
{
Case 1: Statement(s);
Break;
Case 2: Statement(s);
break;
Case 3: Statement(s);
break;
.
.
.
default: Statement(s);
break;
}
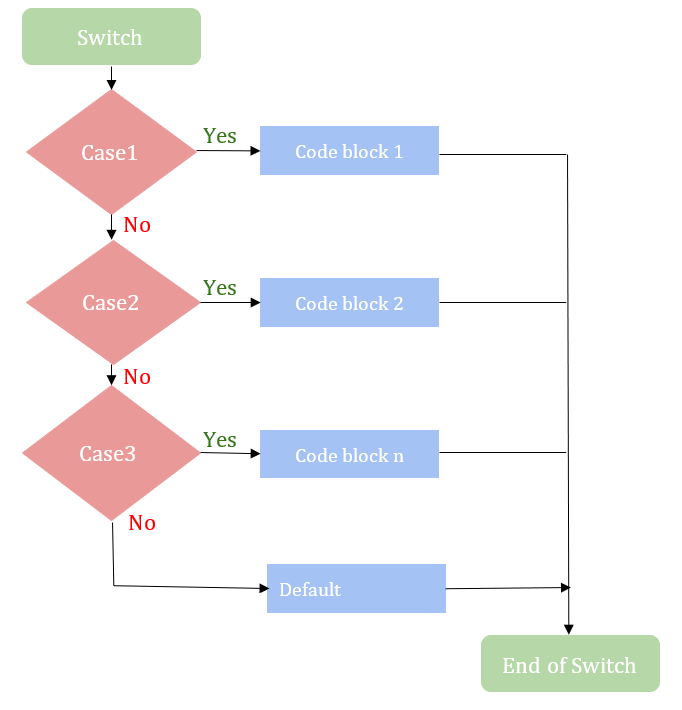
SWITCH 语句流程图
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int day;
printf("Enter the Day: ");
scanf("%d",&day);
switch(day)
{
case 0: printf("Today is Sunday\n");
break;
case 1: printf("Today is Monday\n");
break;
case 2: printf("Today is Tuesday\n");
break;
case 3: printf("Today is Wednesday\n");
break;
case 4: printf("Today is Thursday\n");
break;
case 5: printf("Today is Friday\n");
break;
case 6: printf("Today is Saturday\n");
break;
default: printf("Invalid Day");
}
}
嵌套 switch 语句
switch (variable)
{
case 1:
statement;
switch (variable_1)
{
statement;
}
break;
case 2:
statement;
switch (variable_2)
{
statement;
}
break;
default:
statement;
switch (variable_x)
{
statement;
}
break;
}
? 运算符
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int n,a;
printf("Enter a number:");
scanf("%d",&n);
a = ((n%2==0)?0:1);
if(a==0)
printf("\nEven");
else
printf("\nOdd");
}
Output 1:
Enter a number:6
Even
Output 2:
Enter a number:5
Odd