


二分查找算法又称“半区间算法”或“对数算法”。它可用于从大量元素列表中进行搜索。它在大列表上的工作速度比在顺序搜索中小列表上更快。
该算法首先找到中间元素并将其与搜索项进行比较,如果不同,则将数组分成两部分。一个左子数组,包含中间元素之前的元素,一个右子数组,包含中间元素之后的元素。现在,将根据搜索元素存在的可能性选择其中一个子数组继续搜索。此过程将一直持续到找到结果或子列表的大小减小到零。因此,它使用分而治之的方法在数组中搜索元素。二分查找的最坏情况时间复杂度是 O(logn)。
二分查找算法在已排序的数组中搜索元素。如果给定的数组未排序,则需要先对元素进行排序,然后才能进行搜索。
现在,让我们看看二分查找算法的工作原理。

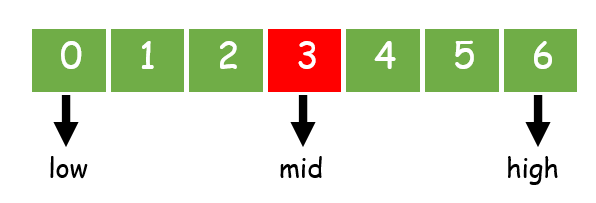
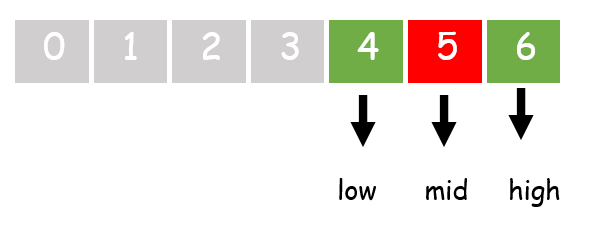

步骤 1:编写一个 `function` binarySearch(),其中包含变量数组 arr 和搜索值 item。
步骤 2:初始化变量 low 为 0,high 为最后一个索引。
步骤 3:启动一个 `while loop`,重复直到条件 low <= high,
步骤 4:找到数组的中间索引 mid,并将中间元素与 item 进行比较,如果匹配则 `return` 中间元素的索引。
步骤 5:检查 item < arr[mid],如果是,则最后一个索引变为 high=mid-1,否则起始索引变为 low=mid+1。
步骤 6:现在以 `return` 0 结束 `function`,表示未找到匹配项。
步骤 7:初始化一个包含值的数组 arr 和要搜索的 item。
步骤 8:对数组进行排序,并使用值 arr、item 调用 binarySearch(),检查 `return` 值并 `cat` 输出适当的结果。
binarySearch = function(arr,item) {
low <- 1; high <- length(arr)
while (low <= high){
mid <- as.integer(round((low + high) / 2))
if (abs(arr[mid] - item) ==0) {
return(mid)
} else if (arr[mid] < item) {
low <- mid + 1
} else {
high <- mid - 1
}
}
return(0)
}
arr <- c(4, 0, 3, 1, 5, 6, 2)
sorted_arr <- sort(arr)
item <- 4
cat("Array ", arr, "\nSorted array ",sorted_arr,"\nitem = ", item, "\n")
index <- binarySearch(sorted_arr, item)
if (index!=0){
cat("Element is present at index ", index, "\n")
}else{
cat("element not found")
}
Array 4 0 3 1 5 6 2 Sorted array 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 item = 4 Element is present at index 5