


在这里,我们讨论一个用 C++ 程序求二次方程所有根的方法。
在数学中,我们将二次方程定义为次数为 2 的方程,这意味着此函数的最高指数为 2。二次方程的标准形式是 y = ax2 + bx + c,其中 a、b 和 c 是数字且 a 不能为 0。
示例:6x2 + 11x – 35 = 0。
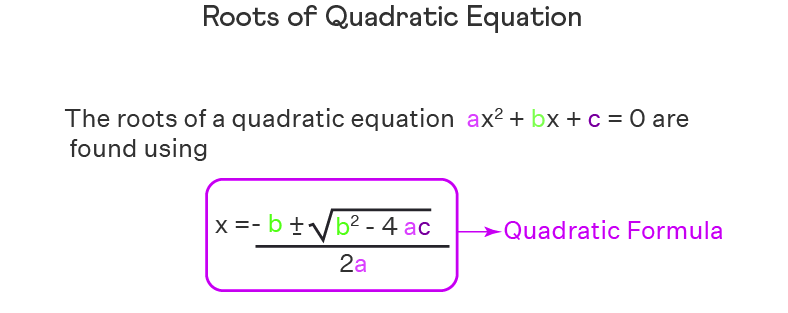
对于二次方程 ax2 + bx + c = 0,根的计算公式为:
x = (-b ± √ (b² - 4ac) ) / 2a
其中,
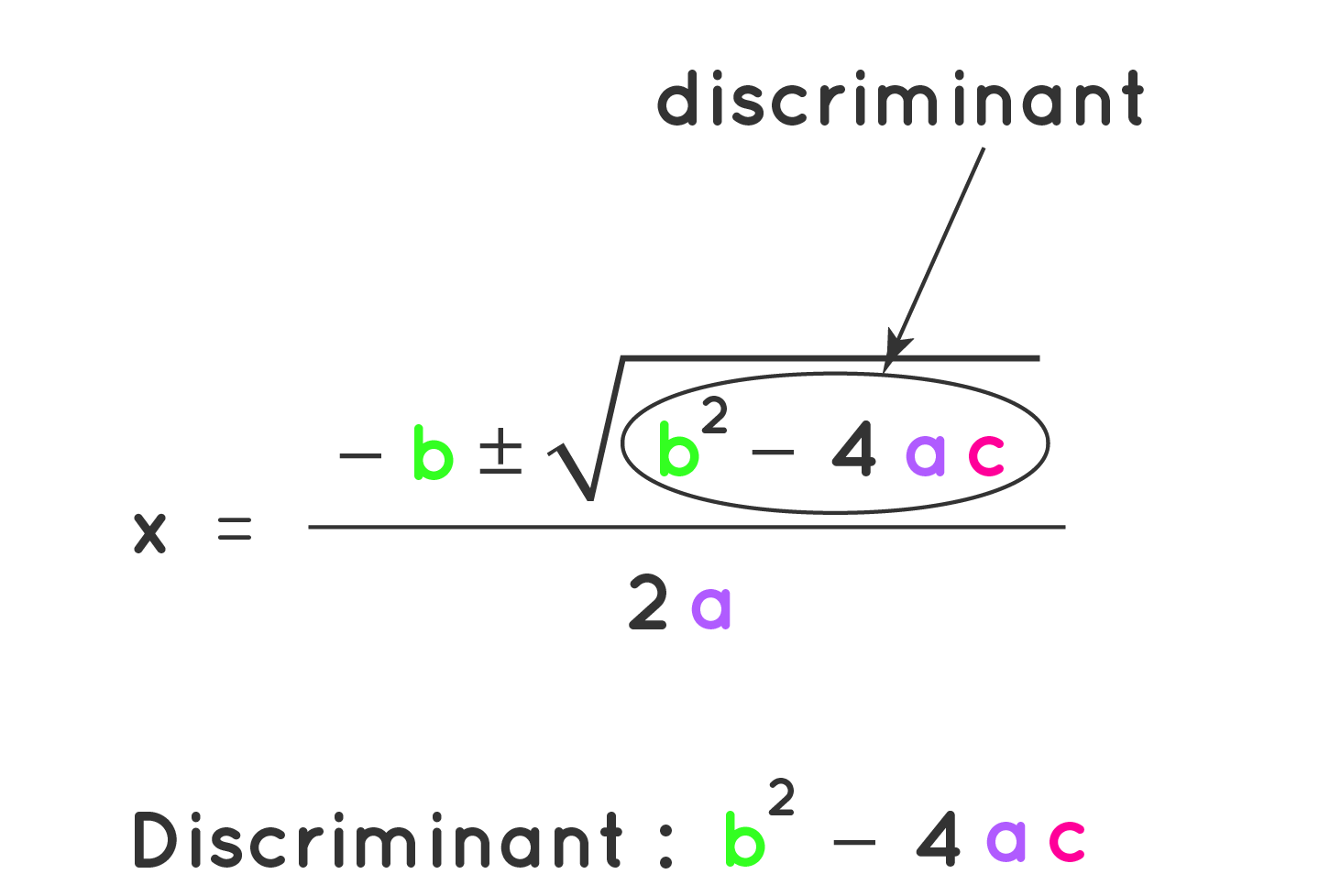
根据判别式的值,方程的根将是:
要求用户输入三个变量 a、b 和 c 的值。首先,使用公式 Discriminant = b² - 4ac 计算判别式的值。将该值存储到浮点型变量 discrim 中。
对于判别式的值,我们有三种情况。正如我们上面讨论的,判别式可以小于、等于或大于零。这可以通过使用 if….else if….else 语句来完成。
如果 discrim 的值大于零 ( discrim > 0 ),则使用公式 (-b ± √ (b² - 4ac) )/2a 计算根。在这个方程中,平方根将使用 sqrt 函数求出。C++ 中的 sqrt() 函数用于计算平方根。它在 C++ 的 cmath 头文件中定义。
否则,如果判别式值等于零 ( discrim == 0 )
否则,根将有实部和虚部。
步骤 1: 调用头文件 iostream。
步骤 2: 调用头文件 cmath.
步骤 3: 使用 namespace std
步骤 4: 打开主函数 int main().
步骤 5: 声明浮点变量;a, b, c, R1, R2, discrim, ipart, rpart
步骤 6: 打印消息以输入系数 a、b 和 c;
步骤 7: 将数字读入变量 a、b 和 c。
步骤 8: 计算判别式 discrim = b² - 4ac。
步骤 9: 如果 discrim > 0
否则如果 discrim = 0
否则如果 discrim < 0
步骤 10: 退出
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main() {
float a, b, c, R1, R2, discrim, rPart, iPart;
cout << "Enter coefficients a, b and c: ";
cin >> a >> b >> c;
discrim= b*b - 4*a*c;
if (discrim> 0) {
R1 = (-b + sqrt(discrim)) / (2*a);
R2 = (-b - sqrt(discrim)) / (2*a);
cout << "Roots are real and different." << endl;
cout << "R1 = " << R1 << endl;
cout << "R2 = " << R2 << endl;
}
else if (discrim == 0) {
cout << "Roots are real and same." << endl;
R1 = -b/(2*a);
cout << "R1 = R2 =" << R1 << endl;
}
else {
rPart = -b/(2*a);
iPart =sqrt(-discrim)/(2*a);
cout << "Roots are complex and different." << endl;
cout << "x1 = " << rPart << "+" << iPart << "i" << endl;
cout << "x2 = " << rPart << "-" << iPart << "i" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Enter coefficients a, b and c: 5 3 6 Roots are complex and different. x1 = -0.3+1.05357i x2 = -0.3-1.05357i