


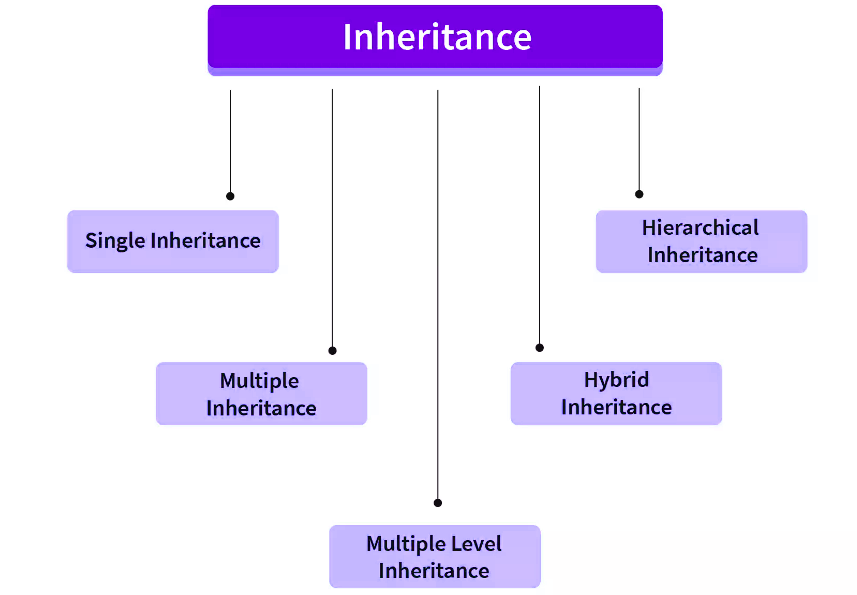
C++ 中主要有五种不同类型的继承
当派生类仅从新的基类继承时,主要发生单一继承。
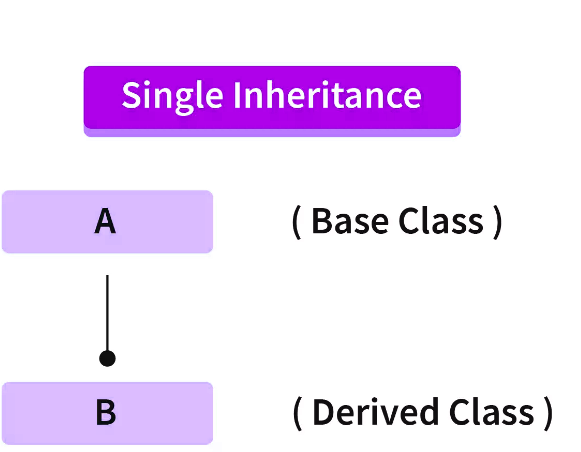
在上图中,A 是基类,B 是派生类;在这种情况下,子类将只继承一个父类。
class Base {
public:
float salary = 1000;
};
class Derived: public Base {
public: float b
void sum() {
cout << " Total Salary is: " << (salary + bonus) << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Derived x;
cout << "Your Salary will be:" << x.salary << endl;
cout << "Your Bonus will be:" << x.bonus << endl;
x.sum();
return 0;
}
输出
Your Salary will be:1000 Your Bonus will be:400 Total Salary is:1400
以上程序的解释
在前面的示例中,Base 是类名,也被认为是父类,其中包含值为 1000 的 salary 属性。
同样,还有另一个名为 Derived 的类,它是子类,它继承了父类的属性,并拥有一个名为 bonus 的属性,其值为 400。
子类中的 Sum() 函数用于将 salary 和 bonus 相加。主函数中的“Derived”类(也是子类)创建了一个名为“x”的对象。通过调用该对象,Derived 类的属性以及 sum 函数,以将 salary 和 bonus 相加,从而产生结果作为输出。
多重继承是指派生类(子类)能够从多个基类(父类)继承的能力。
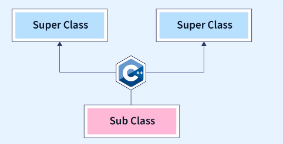
在上面的图中,A 和 B 是基类,C 是从多个基类(父类)派生出来的派生类。
class Base1 {
public:
float salary = 1000;
};
class Base2 {
public: float b
};
class Derived: public Base1, public Base2 {
public:
void sum() {
cout << "Your Total Salary is: " << (salary + bonus) << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Derived x;
x.sum();
return 0;
}
输出
Your Total Salary will be:1400
以上程序的解释
上述程序中存在两个基类 Base1 和 Base2,它们具有 salary 和 bonus 属性。一个名为“derived”的类将从其 Base1 和 Base2 父类继承。派生类中的 sum 函数用于返回 salary 和 bonus 的总和。
在主函数中,使用从派生类形成的名为 x 的对象调用 sum() 函数,该函数将 bonus 和 salary 相加并输出结果。
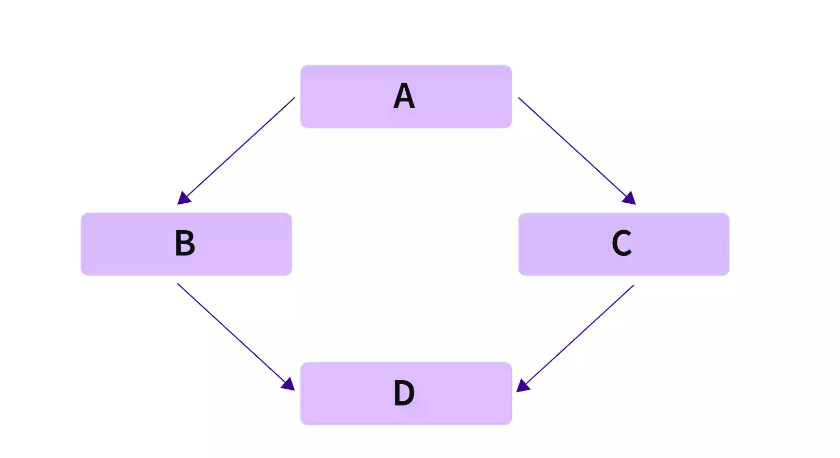
我们可能会在多重继承中遇到菱形问题。让我们看上面的图片作为例子:由于“B”和“C”类都继承自同一个基类“A”,并且“D”同时继承自“B”和“C”,这个问题被称为“菱形问题”,因为它导致形成菱形。
在这种情况下,“B”和“C”类将拥有“A”类的成员变量,因为它们只继承自“A”。由于“D”只继承自“B”和“C”,它也将包含“A”的成员变量的两个副本,一个来自“B”,一个来自“C”,因此导致误解并使编译器混淆在 D 中应该使用“A”的成员变量的哪两个副本。
虚拟继承提供了菱形问题或解决方案。它是一种策略,确保第二级派生(即孙子)只继承超类或基类的成员变量的一个副本。在上面的示例中,由于将类“A”声明为虚拟基类,类“A”的成员变量将只被复制到类“B”和“C”一次。
多级继承是指当一个派生(子)类同时继承基类并作为另一个类的基类(父类)时。在多级继承中,级别或派生类的数量可以是任意的。
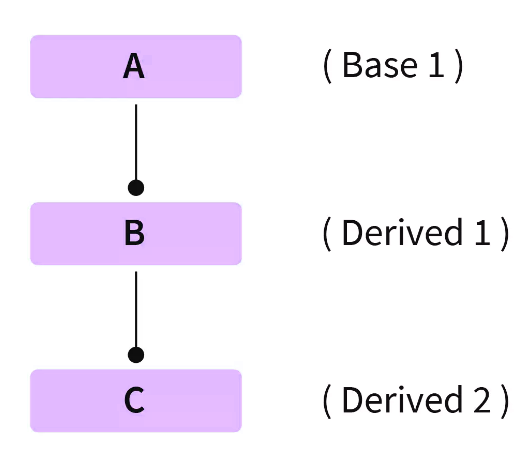
在上图中,类“B”继承自类“A”,并且类“B”现在是类“C”的基类(父类),而类“C”只继承自类“B”。类“A”和“B”的属性现在由类“C”继承。
class BaseClass {
public:
void print() {
cout << " an example of Multilevel Inheritance in C++";
}
};
class DerivedClass: public BaseClass {};
// class which is derived from another derived class
class DerivedClass2: public DerivedClass {};
int main() {
DerivedClass2 Obj;
Obj.print();
return 0;
}
输出
an example of Multilevel Inheritance in C++
以上程序的解释
上述程序中有一个名为 BaseClass 的基类,其中包含消息。这是一个多级继承的示例;基类(父类)由名为 DerivedClass 的派生类继承,而随后的名为 DerivedClass2 的派生类由先前的派生类继承。
在主方法中生成了一个名为 obj 的 DerivedClass2 对象,并且该对象调用基类(顶级父类)的 print 函数,这证明了 DerivedClass2 如何继承 BaseClass 和 DerivedClass 属性。
分层继承是指多个类从一个基类派生属性的过程。
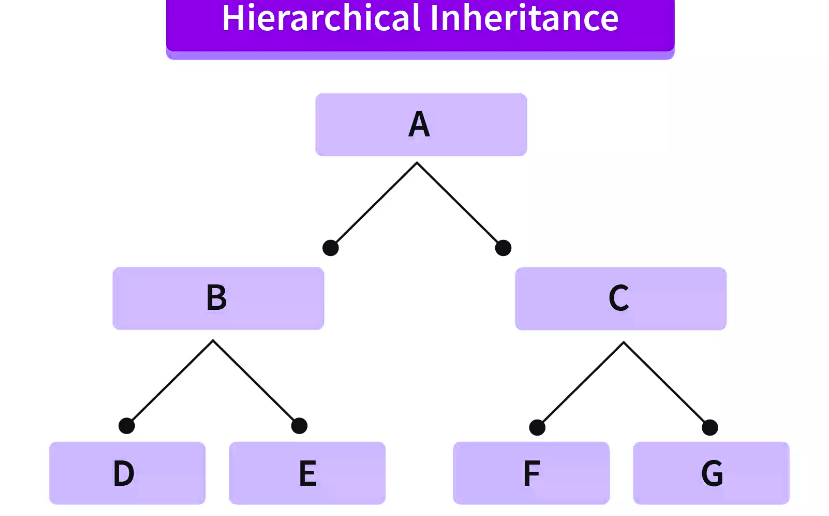
在上面的图中,“A”作为基类,而“B”和“C”是从父类“A”派生出来的派生类。“D”和“E”是从类“A”派生出来的基类“B”继承的派生类,而“E”和“G”是从类“A”派生出来的基类“C”继承的派生类。
class Single_base_class {
public:
int x, y;
void data() {
cout << "\nPlease enter the value of x and y ->\n";
cin >> x << y;
}
};
// class derived1 is just derived from the single_base_class
class Derived1: public Single_base_class {
public:
void product() {
cout << "\nThe Product is= " << x * y;
}
};
//class derived1 is also derived from the class single_base_class
class Derived2: public Single_base_class {
public:
void sum() {
cout << "\nThe Sum is= " << x + y;
}
};
int main() {
Derived1 obj1;
Derived2 obj2;
obj1.data();
obj1.product();
obj2.data();
obj2.sum();
return 0;
}
输出
Please enter the value of x and y: 3 3 The Product is= 9 Enter the value of x and y: 10 10 The Sum is= 20
以上程序的解释
在上面的示例中,有一个名为“单一基类”的基类,它包含一个数据函数,该函数将收集用户输入。基类“单一基类”有一个名为“Derived1”的派生类,它将扩展基类“单一基类”。Derived1 类有一个 product 函数,用于将两个值相乘,在本例中为“x”和“y”。另一个额外的派生类“Derived2”也派生自“单一基类”,它包含 sum 函数以将整数相加。在主函数中,创建并使用了一个对象来调用派生类函数,从而产生上面显示的输出。
在 C++ 中,混合继承结合了一种或多种类型的继承。
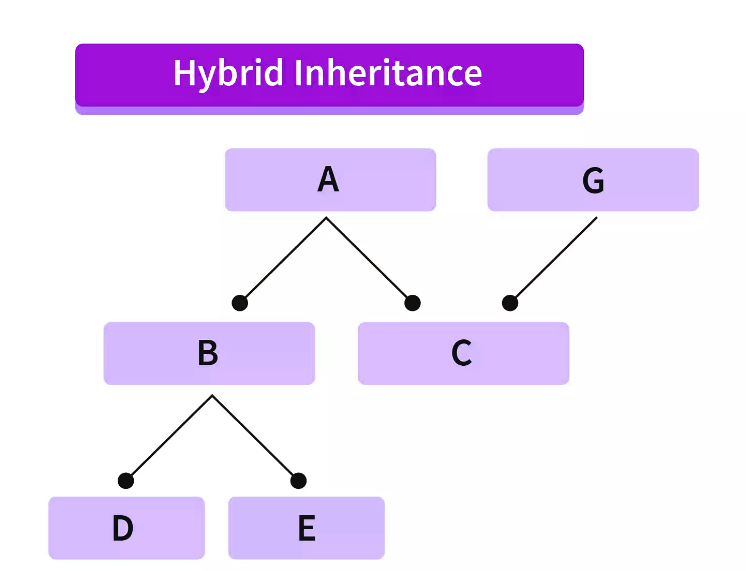
在上面的图中,我们可以看到多种继承类型,或者不同继承类型的组合。
class World {
public:
World() {
cout << "This is our World!\n";
}
};
//here is Single Inheritance
class Continent: public World {
public:
Continent() {
cout << "This is our Continent\n";
}
};
class Country {
public:
Country() {
cout << "This is our Country\n";
}
};
// here is multiple Inheritance
class India: public Continent, public Country {
public:
India() {
cout << "This is India!";
}
};
int main() {
India myworld;
return 0;
}
输出
This is our World! This is our Continent This is our Country This is India!
以上程序的解释
在上面所示的程序中,有一个名为 World 的基类,以及一个扩展“World”的名为 Continent 的派生类。这是一个单一继承的示例。India 是一个派生类,它继承了基类 Country 的“Continent”和“Country”类,在这里我们能够看到多重继承。因此,在这种情况下,展示了混合继承。
结论
我们回顾了各种类型的继承以及它们如何被恰当地利用。继承是编程中的一个基本思想,因为它促进了代码的可重用性和可靠性。