


在本 C++ 教程中,您将学习向函数传递参数的两种不同方式(值传递和引用传递),以及它们如何有用和不同。
C 语言中的函数参数是在调用函数时使用的一组变量。通常,参数接收输入值并将它们传递给函数定义中的相应参数。 通常有两种方法可以将参数传递到函数中:
在继续讨论这两种方法之前,让我们先熟悉一下传递参数时使用的另外两个重要术语。它们是:
形式参数是在定义函数时使用的。而实际参数则在函数被调用执行时起作用。因此,形式参数设定规则,实际参数将其放入值以产生结果。为了更清楚地说明,请参见下面的可视化。
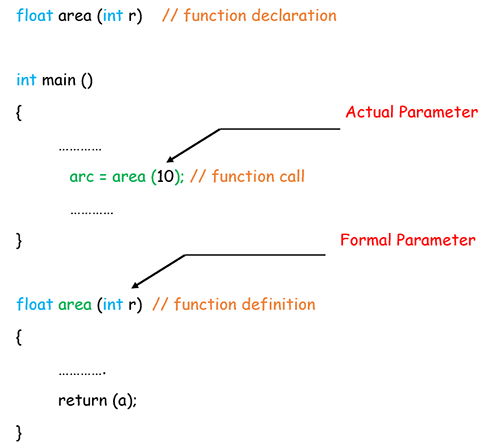
使用此技术,参数的实际值被复制到函数的形式参数中。在这种情况下,在函数内对参数所做的更改不会影响参数。
在向函数传递参数时,值传递方法会将参数的实际值复制到形式参数中。在这种情况下,在函数内对参数所做的更改不会影响参数。
值传递是 C++ 中默认的参数传递方法。这通常表示函数内的代码在调用函数时无法更改传递给函数的参数。请看 **swap()** 函数的定义。
// function definition to swap the values.
void swap(int x, int y) {
int temp;
temp = x; /* save the value of x */
x = y; /* put y into x */
y = temp; /* put x into y */
return;
}
现在,让我们通过传递实际值来调用 **swap()** 函数,如下例所示。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// function declaration
void swap(int x, int y);
int main () {
// local variable declaration:
int a = 1000;
int b = 2000;
cout << "Before swap, value of a :" << a << endl;
cout << "Before swap, value of b :" << b << endl;
// calling a function to swap the values.
swap(a, b);
cout << "After swap, value of a :" << a << endl;
cout << "After swap, value of b :" << b << endl;
return 0;
}
当给定的代码在一个文件中组合、编译和执行时,将获得以下结果:
Before swap, value of a :1000 Before swap, value of b :2000 After swap, value of a :1000 After swap, value of b :2000
这表明,尽管值在函数内部被修改了,但它们并未改变。
使用此技术,参数的地址被复制到形式参数中。该地址在函数内部用于获取调用期间使用的实际参数。这意味着对参数的更改会影响参数。
在调用函数时,参数的地址被复制到形式参数中,通过传递参数的指针方法。该地址在函数内部用于获取调用期间使用的实际参数。这意味着对参数的更改将影响传递的参数。
为了通过指针传递值,参数指针以与传递其他值相同的方式传递给函数。因此,函数参数必须声明为指针类型,如以下 swap() 函数所示,该函数交换其参数指向的两个整数变量的值。
// function definition to swap the values.
void swap(int *x, int *y) {
int temp;
temp = *x; /* save the value at address x */
*x = *y; /* put y into x */
*y = temp; /* put x into y */
return;
}
现在,让我们通过传递指针来调用 **swap()** 函数,如下例所示。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// function declaration
void swap(int *x, int *y);
int main () {
// local variable declaration:
int a = 1000;
int b = 2000;
cout << "Before swap, value of a :" << a << endl;
cout << "Before swap, value of b :" << b << endl;
/* calling a function to swap the values.
* &a indicates pointer to a ie. address of variable a and
* &b indicates pointer to b ie. address of variable b.
*/
swap(&a, &b);
cout << "After swap, value of a :" << a << endl;
cout << "After swap, value of b :" << b << endl;
return 0;
}
Before swap, value of a :1000 Before swap, value of b :2000 After swap, value of a :1000 After swap, value of b :2000
此方法将参数的引用复制到形式参数中。该引用在函数内部用于获取调用中使用的实际参数。这意味着对参数的更改会影响参数。
要按引用传递值,参数引用就像任何其他值一样传递给函数。因此,函数参数必须声明为引用类型,如以下 swap() 函数所示,该函数交换其参数指向的两个整数变量的值。
// function definition to swap the values.
void swap(int &x, int &y) {
int temp;
temp = x; /* save the value at address x */
x = y; /* put y into x */
y = temp; /* put x into y */
return;
}
现在,让我们通过按引用传递来调用 **swap()** 函数,如下例所示。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// function declaration
void swap(int &x, int &y);
int main () {
// local variable declaration:
int a = 1000;
int b = 2000;
cout << "Before swap, value of a :" << a << endl;
cout << "Before swap, value of b :" << b << endl;
/* calling a function to swap the values using variable reference.*/
swap(a, b);
cout << "After swap, value of a :" << a << endl;
cout << "After swap, value of b :" << b << endl;
return 0;
}
Before swap, value of a :1000 Before swap, value of b :2000 After swap, value of a :2000 After swap, value of b :1000