


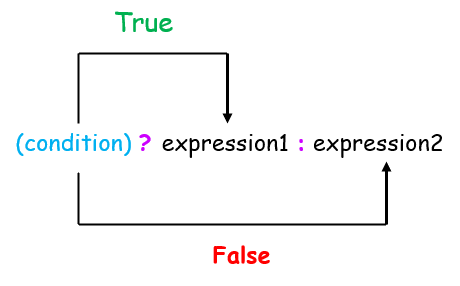
在 C++ 中,条件运算符在条件为真时返回一个值,在条件为假时返回另一个值。此运算符也称为三元运算符。
(condition) ? true_value : false_value;
在上述语法中,条件将写入条件位置;如果条件为真,则执行真值;如果条件为假,则执行假值。
现在考虑一个示例以更好地理解。
在 C++ 程序中使用条件运算符来查找两个整数变量值之间的最大数。
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=20,b=7,c;
c=(a>b) ? a : b;
cout<<"Greatest number is "<<c;
return 0;
}
输出
Greatest number is 20
因为条件 (a>b) 为真,所以紧接在 ? 标记之后编写的语句将执行,并且 a 的值将存储在 c 中。
通过将条件表达式作为三元运算符的第二部分(在?之后)或第三部分(在:之后)添加,可以创建嵌套条件运算符。
1.(condition) ? ((condition) ? true_value : false_value) : false_value;
2.(condition) ? true_value : ((condition) ? true_value : false_value);
在上述两种语法的第 1 行,您可以看到如果第一个条件为真,我们将在第一个条件中的 ? 标记之后立即检查另一个条件。同样,在第 2 行,如果第一个条件为真,则执行真值;如果为假,我们将在第一个条件中的 : 标记之后立即检查另一个条件。
使用嵌套条件运算符,编写了一个 C++ 程序来查找三个整数变量值中的最大数。
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=20,b=50,c=26,g;
c=(a>b && a>c) ? a : ((b>a && b>c) ? b : c);
cout<<"So the greatest number is "<<c;
return 0;
}
输出
So the greatest number is 50
条件 (a>b && a>c) 在此处为 假,因此我们检查另一个条件 (b>a && b>c),该条件紧接在第一个条件的 : 标记之后编写,并且此次条件为真,因此 b 的值存储在 c 中。