


众所周知,C++是一种面向对象编程语言。因此,我们可以使用类和对象来降低复杂性,同时它还提高了程序中代码的可重用性。构造函数和析构函数是帮助我们实现此目的的两个基本类特性。
通过简单的示例,我们将学习 C++ 构造函数及其类型。
构造函数是一种非常特殊的成员函数,它与类同名,没有返回类型,并且在创建类的新实例时自动调用。
每次创建类对象时,作为成员函数的构造函数都会自动调用,并且每个对象都由一个特殊的类函数执行,该函数称为构造函数。每次创建对象时,编译器都会调用构造函数。构造函数主要在为对象分配存储空间后,为对象成员赋值或初始化。
在 C++ 中,构造函数是一种特殊方法,每当创建类对象时都会自动调用。
语法
创建构造函数时,在类名后使用括号 ()。
构造函数可以在类声明内部和外部定义:-
以下是在类中指定构造函数的语法
以下是在类外部指定构造函数的语法
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class student {
int rno;
char name[20];
double fee;
public:
student()
{
cout << "please enter the RollNo:";
cin >> rno;
cout << "Please enter the Name:";
cin >> name;
cout << "Please enter the Fee:";
cin >> fee;
}
void display()
{
cout << endl << rno << "\t" << name << "\t" << fee;
}
};
int main()
{
student s; // automatically constructor will be called when
// we create object of the class
s.display();
return 0;
}
输出
please enter the RollNo:25 Please enter the Name:John Please enter the Fee:10000 25 John 10000
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class student {
int rno;
char name[50];
double fee;
public:
student();
void display();
};
student::student() {
cout << " Please Enter the RollNo:";
cin >> rno;
cout << "Please Enter the Name:";
cin >> name;
cout << "Please Enter the Fee:";
cin >> fee;
}
void student::display() {
cout << endl << rno << "\t" << name << "\t" << fee;
}
int main() {
student s;
s.display();
return 0;
}
输出
Please Enter the RollNo:12 Please Enter the Name:James Please Enter the Fee:12000 12 James 12000
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyClass { // The class
public: //Is the access specifier
MyClass() { // Constructor
cout << "Hello Students!";
}
};
int main() {
MyClass myObj; //Create an object of MyClass (so this will surely call the constructor)
return 0;
}
输出
Hello Students!
在上面的示例中,构造函数与类同名,它是公共的,并且没有任何返回类型。
以下是构造函数与常规/普通函数的一些区别
例如
class A {
public:
// constructor
A() {
// object initialization
}
};
在这种情况下,类 A 的构造函数由函数 A() 表示。
应该注意,创建者
构造函数分为三种不同类别
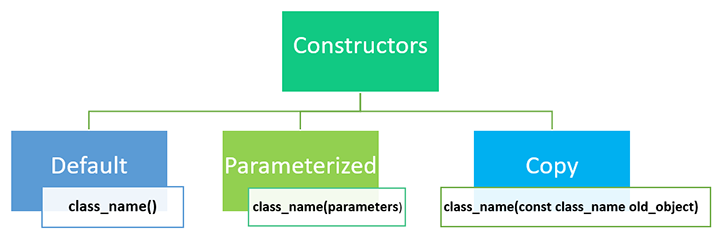
让我们使用一个实际示例来更好地理解 C++ 中不同类型的构造函数。
想象一下你去了商店买一个包。当你想要买一个包时,有哪些可能性?第一次,你在商店里要一个包。给我一个包意味着你没有指定品牌名称或颜色;你只说你想要一个包。因此,如果我们只是说“我想要一个包”,他就会给我们市场上或他店里最受欢迎的包,默认构造函数也是如此。
第二种选择是走进商店,并指定你想要一个 ABC 品牌蓝色的包。所以你提到了,他给了你包。因此,在这种情况下你指定了参数。参数化构造函数就是这样!
第三种情况是当你去商店并声明“我想要一个像这样的包”(你手里拿着一个实物包)。这样,店主就会注意到那个包,他会给你一个新包。然后店主会给你一个那个包的精确副本。拷贝构造函数就是这样!
不接受任何参数的构造函数称为默认构造函数。它有零个参数。它主要在创建对象时调用。
语法
class_name ( ) ; ................................................. (1)
class_name :: class_name ( ) body................... (2)
class_name() = delete ;...................................... (3)
class_name() = default ;.................................... (4)
class_name :: class_name ( ) = default ;.......... (5)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Employee
{
public:
Employee()
{
cout<<"Default Constructor Is Invoked"<<endl;
}
};
int main(void)
{
Employee e1; //creating an object of an Employee
Employee e2;
return 0;
}
输出
Default Constructor Is Invoked Default Constructor Is Invoked
让我们编写一个 C++ 程序来理解默认构造函数的概念。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class construct {
public:
int a, b;
// Default Constructor
construct()
{
a = 80;
b = 100;
}
};
int main()
{
// Default constructor will be called automatically
// when an object is created
construct c;
cout << "a: " << c.a << endl << "b: " << c.b;
return 1;
}
输出
a: 80 b: 100
参数可以传递给构造函数。当对象形成时,这些参数通常有助于初始化它。为了制作一个参数化构造函数,只需像任何其他函数一样为其添加参数。定义构造函数体时,应该使用参数初始化对象。
让我们编写一个 C++ 程序来理解参数化构造函数的概念。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point {
private:
int x, y;
public:
// Parameterized Constructor
Point(int x1, int y1)
{
x = x1;
y = y1;
}
int getX() { return x; }
int getY() { return y; }
};
int main()
{
// Constructor called
Point p1(100, 105);
// Access the values assigned by a constructor
cout << "p1.x = " << p1.getX()
<< ", p1.y = " << p1.getY();
return 0;
}
输出
p1.x = 100, p1.y = 105
参数化构造函数有什么用途?
在本教程中,我们通过适当的示例解释了 C++ 构造函数和构造函数类型。拷贝构造函数也是构造函数的一种类型,将在下个教程中进行解释。