


在之前的教程中,我们详细讨论了 for 循环、while 循环和 do-while 循环 的使用。正如我们在之前的教程中讨论的,当迭代次数已知时,我们将在 C++ 中使用 for 循环。当迭代次数未知但循环终止条件已知时,我们将在 C++ 中使用 while 循环。如果代码需要至少执行一次,例如在菜单驱动程序中,那么我们将使用 do-while 循环。
在本教程中,让我们讨论 C++ 中更高级的循环技术。C++ 中更高级的循环技术包括:
本主题将介绍 C++ 编程语言中基于范围的 for 循环。在 C++11 及更高版本中,C++ 语言引入了基于范围的 for 循环这一新概念,它比常规的 for 循环要好得多。基于范围的 for 循环无需大量编码即可实现 for 循环迭代。它是一个顺序迭代器,可迭代容器的每个元素(从头到尾)。
语法
for (range_declaration : range_expression )
{
loop statement
}
例如,
// initialize an int array
int num_array[3] = {1, 2, 3};
// use of ranged for loop
for (int i: num_array) {
// code
}
在上面的例子中,
int i 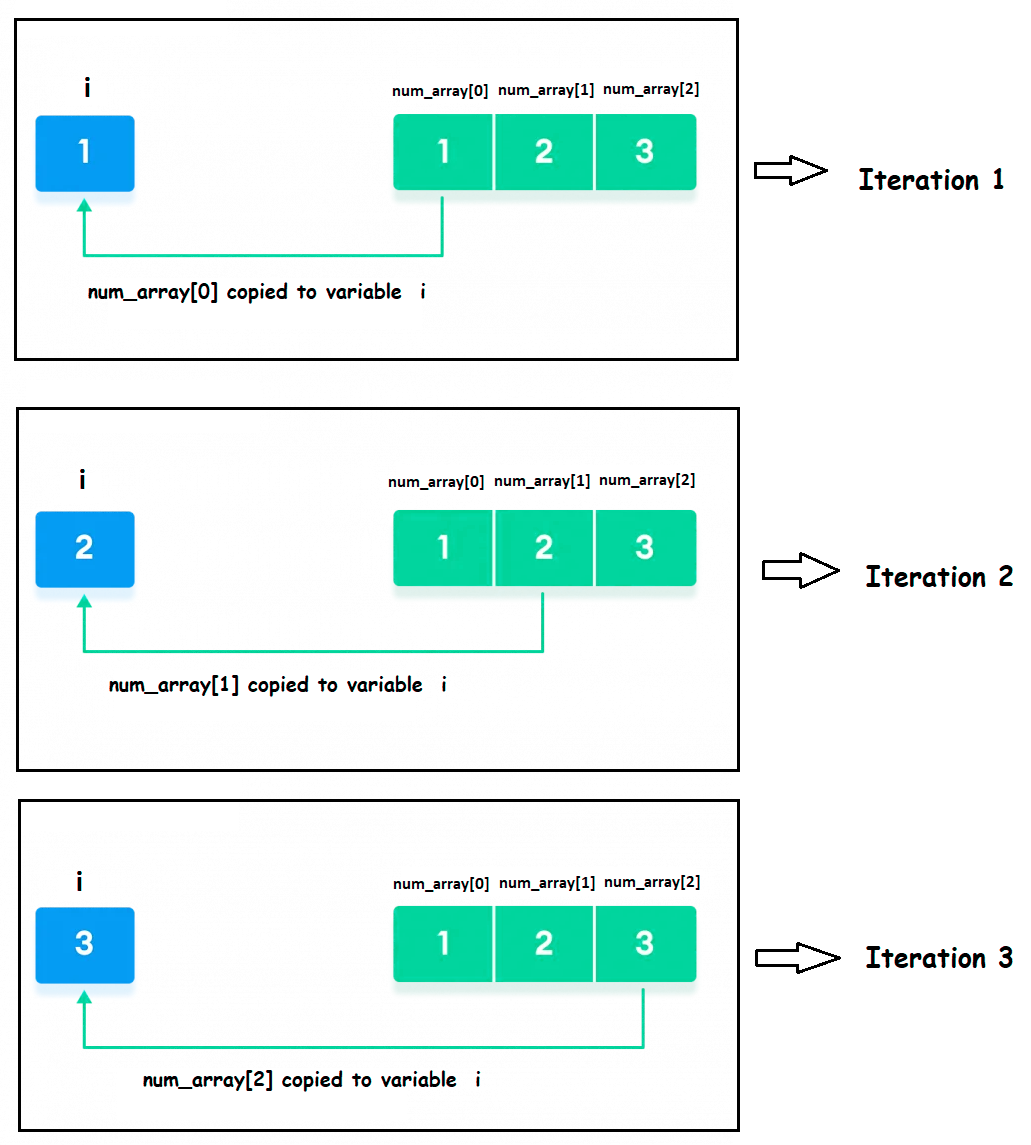
注意: 假设我们不知道容器元素的数据类型,我们可以使用 auto 关键字,它会自动确定范围表达式的数据类型。
让我们看一个 C++ 基于范围的 for 循环示例,它打印一个 int 和 double 数组
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int int_array[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
double double_array [5] = { 4.2, 5.7, 4.8, 8.5, 4.0 };
// use range based for loop
for ( const auto &var : int_array)
{
cout << var << " " ;
}
// use auto keyword to automatically specify the data type of darr container.
for ( const auto &var : double_array)
{
cout << var << " " ;
}
return 0;
}
输出
100 200 300 400 500 4.2 5.7 4.8 8.5 4.0
让我们看一个 C++ 基于范围的 for 循环示例,它打印向量元素。
向量只是一个动态大小的数组。它包含数量几乎无限的同类项(即相同类型的对象),可以通过它们在列表中的位置轻松访问。您无需显式使用 new int[size] 或 delete[] my array 等命令,因为底层数组会根据需要自动调整大小。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x; // declare integer variable
// declare vector variable
vector <int> vect = {10, 15 , 20, 25, 30};
// display vector elements
for ( int x : vect)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出
10 15 20 25 30
当一个循环定义在另一个循环的主体内部时,它被称为嵌套 for 循环。同样,在一个基于范围的循环内部定义另一个基于范围的循环被称为嵌套的基于范围的 for 循环。
语法:
for ( int x : range_expression) // outer loop
{
for ( int y : range_expression) // inner loop
{
// statement to be executed
}
// statement to be executed
}
在上面的语法中,我们定义了一个嵌套在另一个循环中的基于范围的 for 循环。在 C++ 中,这被称为内部和外部基于范围的 for 循环。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main () { int arr1[5] = { 0, 1, 2, 3,4 }; int arr2[6] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,6 }; // use nested range based for loop for ( int x : arr1 ) { // declare nested loop for ( int y : arr2 ) { cout << " x = " << x << " and j = " << y << endl; } } return 0; }
输出
x = 0 and j = 1 x = 0 and j = 2 x = 0 and j = 3 x = 0 and j = 4 x = 0 and j = 5 x = 0 and j = 6 x = 1 and j = 1 x = 1 and j = 2 x = 1 and j = 3 x = 1 and j = 4 x = 1 and j = 5 x = 1 and j = 6 x = 2 and j = 1 x = 2 and j = 2 x = 2 and j = 3 x = 2 and j = 4 x = 2 and j = 5 x = 2 and j = 6 x = 3 and j = 1 x = 3 and j = 2 x = 3 and j = 3 x = 3 and j = 4 x = 3 and j = 5 x = 3 and j = 6 x = 4 and j = 1 x = 4 and j = 2 x = 4 and j = 3 x = 4 and j = 4 x = 4 and j = 5 x = 4 and j = 6
传统 for 循环用于重复执行代码块,直到满足指定条件。传统 for 循环有三个参数:变量初始化、条件指定和在条件保持为真时递增的计数器。另一方面,C++ 11 及更高版本包含新的基于范围的 for 循环。它有两个参数:范围声明和范围表达式。它也用于反复执行代码块。