在本教程中,您将学习 Go 编程语言中的不同数据类型。到目前为止,我们讨论了变量,每个变量都与一个数据类型相关联,该数据类型持有一些值。Golang 支持数字、字符、布尔等**基本数据类型**,以及使用 int、float 等基本数据类型构建的用户定义**复合数据类型**。在本教程中,我们将详细介绍这两种数据类型的不同分类,并详细了解 Golang 中的每种数据类型。
在编程语言中,数据类型是一种分类,用于指定变量所包含的数据的类型。
为任何变量定义的数据类型告诉编译器,在 Golang 程序执行期间,程序员声明的变量打算如何使用。因此,变量的所有值都有一个静态类型,Go 语言可以被称为静态类型编程语言。
数据类型可以通过**关键字 var** 声明变量,或通过**关键字 const** 声明常量,可以单行或多行声明。语法中的 **<type>** 占据了 Golang 中的基本数据类型。让我们在下一节中讨论基本数据类型。通过下面的例子,回顾一下变量如何使用 const 和 var 关键字来定义其类型,为了更好地理解,请参考(Golang 常量 和 Golang 变量 教程)。
示例 1:声明带数据类型的变量的语法
var <variable_name> <type> = <value> //var keyword
Or
const <variable_name> <type> = <value> //const keyword
Or
var <variable_name1>,<variable_name2> <type> //Multiple variable declaration
Or
<variable_name1>,<variable_name2> := <value1><value2>
//short variable declaration
Golang 中的数据类型分为两类
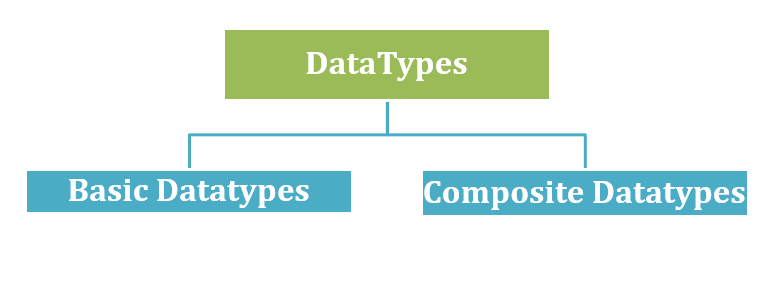
一个**基本类型**是构成基本构建块的数据类型。它是一种**原始数据类型**。GO 语言支持整数、浮点数、字符串、布尔和复数等基本数据类型。
一个**复合数据类型**是由原始数据类型和其他复合类型构建的数据类型。它也称为**组合数据类型**。
基本数据类型主要分为
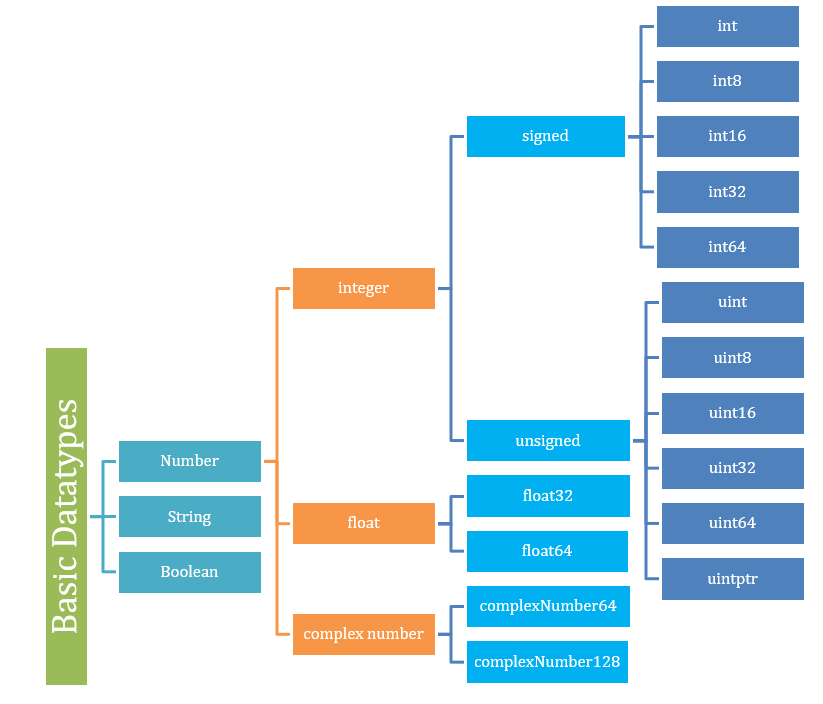
让我们详细了解每种基本数据类型
数字或数值数据类型表示**整数**、**浮点数**和**复数**。例如整数如 34、345 等,带小数点的浮点数如 45.89、5.8 等,以及形式为 a+bi 的复数,如 34 + 78i。
让我们从数值数据类型开始。编程中有三种主要的数值类型
整数数据类型是表示一组二进制数字(位)的整数范围。在 Golang 中,整数可以是正数、负数或零。
基本整数数据类型进一步分为
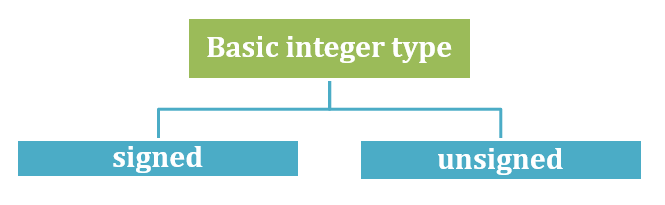
“int” 表示有符号整数,“uint” 表示无符号整数
有符号整数数据类型是默认类型,它依赖于机器,支持 32 位(4 字节)和 64 位(8 字节)机器。这种数值数据类型存储正值和负值,它们有 5 种不同的大小(类型),具有不同的范围。
| int | int8 | int16 | int32 | int64 |
下表详细说明了有符号数据类型的类型、大小和各种范围。
| 类型 | 大小 | 范围 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 32 位/4 字节或 64 位/8 字节 | |
| int8 | 8 位/1 字节 | -128 到 127 |
| int16 | 16 位/2 字节 | -32768 到 32767 |
| int32 | 32 位/4 字节 | -2147483648 到 214748367 |
| int64 | 64 位/8 字节 | -9223372036854775808 到 9223372036854775807 |
从表中推断:**int8** 是一个有符号整数,其值范围从 -128 到 127,int16 是一个有符号整数,其值范围从 -32768 到 32767,等等。
让我们讨论所有类型的有符号整数数据类型,以及它们在 Golang 中如何使用相应的语法声明
var a int //declares variable a of int integer type
var a int8 //declares variable a of integer type int8
var a int16 //declares variable a of integer type int16
var a int32 //declares variable a of integer type int32
var a int64 //declares variable a of integer type int64
让我们通过两个程序示例来理解如何使用不同的 int 数据类型。使用 int 声明既简单又容易;在早期的教程中提到了许多使用此数据类型的 Golang 程序。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
//Declare a int 8
var Type1 int8 = 6
//Declare a int16
var Type 2 int16 = 6
//Size of int8 in bytes
fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(Type1))
fmt.Printf("Type1's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(Type1))
//Size of int16 in bytes
fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(Type2))
fmt.Printf("Type2's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(Type2)
}
输出
1 bytes Type1's type is int8 2 bytes Type2's type is int16
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
//Declare a int32
var Type3 int32 = 6
//Declare a int64
var Type4 int64 = 6
//Size of int32 in bytes
fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(Type3))
fmt.Printf("Type3's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(Type3))
//Size of int64 in bytes
fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(Type4))
fmt.Printf("Type4's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(Type4))
}
输出
4 bytes Type3's type is int32 8 bytes Type4's type is int64
无符号整数数据类型 (**uint**) 是默认类型,它依赖于机器,支持 32 位(4 字节)和 64 位(8 字节)机器。这种数值数据类型只保存非负值,它们有 6 种不同的大小(类型)和各种范围。
| uint | uint8 | uint16 | uint32 | uint64 | uintptr |
| 类型 | 大小 | 范围 |
|---|---|---|
| uint | 32 位/4 字节或 64 位/8 字节 | 0 到 4294967295 或 |
| uint8 | 8 位/1 字节 | 0 到 255 |
| uint16 | 16 位/2 字节 | 0 到 65535 |
| uint32 | 32 位/4 字节 | 0 到 4294967295 |
| uint64 | 64 位/8 字节 | 0 到 18446744073709551615 |
| uintptr | 未解释的位 | 指针值 |
上表详细说明了无符号数据类型的类型、大小和各种范围。从表中进行推断。
uint8 是一个无符号整数,其值范围从 0 到 255,uint16 是一个无符号整数,其值范围从 0 到 65535,等等。uintptr 是一个无符号整数数据类型,其大小足以容纳指针值的未解释位。声明 uint 整数数据类型的语法
var a uint //declares variable a of unsigned integer type uint
var a uint8 //declares variable an of integer type uint8
var a uint16 //declares variable an of integer type uint16
var a uint32 //declares variable an of integer type uint32
var a int64 //declares variable an of integer type uint64
uintptr
让我们通过两个程序示例来理解如何使用不同的 uint 数据类型
package main import ( "fmt" "reflect" "unsafe" ) func main() { //Declare a uint8 var type1 uint8 = 2 //Size of uint8 in bytes fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(type1)) fmt.Printf("type1's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(type1)) //Declare a uint16 var type 2 uint16 = 2 //Size of uint16 in bytes fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(type2)) fmt.Printf("type2's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(type2)) }
输出
1 bytes Type1's type is uint8 2 bytes Type2's type is uint16
package main import ( "fmt" "reflect" "Unsafe" ) func main() { //Declare a uint32 var type3 uint32 = 2 //Size of uint8 in bytes fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(type3)) fmt.Printf("type3's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(type3)) //Declare a uint64 var type4 uint64 = 2 //Size of uint16 in bytes fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(type4)) fmt.Printf("type4's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(type4)) }
输出
4 bytes Type3's type is uint32 8 bytes Type4's type is uint64
浮点是一种数值数据类型,表示小数值,如 45.6、0.00005666
在 Golang 中,浮点数分为两种类型:Float32 和 Float64。
| 类型 | 大小 | 范围 (Range) |
|---|---|---|
| Float32 | 32 位/4 字节 | -3.4e+38 到 3.4e+38 |
| Float64 | 64 位/8 字节 | -1.7e+308 到 +1.7e+308 |
Float32 是 32 位的浮点数据类型
用于声明 float32 数据类型的语法是
var a float32
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
//Declare a float32
var a float32 = 2
//Size of float32 in bytes
fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(a))
fmt.Printf("a's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(a))
}
输出
4 Bytes a's type is float32
Float64 是一个 64 位的浮点数据类型
用于声明 float64 数据类型的语法是
var a float64
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
//Declare a float64
var a float64 = 2
//Size of float64 in bytes
fmt.Printf("%d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(a))
fmt.Printf("a's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(a))
//Default is float64 when you don't specify a type
b := 2.3
fmt.Printf("b's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(b))
}
输出
8 Bytes a's type is float64 b's type is float64
注意: 使用任何浮点数对变量进行短声明时,会将其检测为 float64 数据类型。如果未指定类型,则 Float64 是默认数据类型。
复数的形式为 a+ib,其中 **a** 是实部,**ib** 是虚部。
复数可以通过两种方式初始化
complex(a,b)
var a int64 //declares variable a of integer type int64
A := 9 + 20i
在 Golang 中,复数有两种数据类型:Complex64 和 Complex128
| 类型 | 特性 |
|---|---|
| Complex64 | 实部和虚部由 Float32 构成 |
| Complex128 | 实部和虚部由 Float64 构成 |
实部和虚部的大小是 float32 类型,即 32 位或 4 字节。
complex64 的范围与 float32 相同,即 1.2E-38 到 3.4E+38
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
var a float32 = 7
var b float32 = 2
//Initialize-1
c := complex(a, b)
//Initialize-2
var d complex64
d = 4 + 5i
//Print Size
fmt.Printf("c's size is %d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(c))
fmt.Printf("d's size is %d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(d))
//Print type
fmt.Printf("c's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(c))
fmt.Printf("d's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(d))
//Operations on complex number
fmt.Println(c+d, c-d, c*d, c/d)
}
上面给出的程序使用了初始化方法来将任何变量初始化为复数。两个变量 a 和 b 被声明为 float32 类型,然后通过 complex() 赋给变量 c。所以现在 c 包含一个 complex64 类型的变量,因为变量 a 和 b 的声明使用了 float32 类型。接下来,一个变量 d 被声明为 complex64 数据类型,并使用简写声明直接赋一个复数值,即
d := 4 + 5i
输出
c's size is 8 bytes d's size is 8 bytes c's type is complex64 d's type is complex64 (11+7i) (3-3i) (18+43i) (0.9268293-0.6585366i)
实部和虚部的大小是 float64 类型,即 64 位或 8 字节。
complex128 的范围与 float64 相同,即 -1.7E+308 到 +1.7E+308
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
var a float64 = 3
var b float64 = 5
//Initialize-1
c := complex(a, b)
//Initialize-2. When don't specify a type , the default type will be complex128
d := 4 + 5i
//Print Size
fmt.Printf("c's size is %d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(c))
fmt.Printf("d's size is %d bytes\n", unsafe.Sizeof(d))
//Print type
fmt.Printf("c's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(c))
fmt.Printf("d's type is %s\n", reflect.TypeOf(d))
//Operations on complex number
fmt.Println(c+d, c-d, c*d, c/d)
}
使用 var 关键字将 a = 3 和 b = 5 赋值为 float64 类型。函数调用 complex() 将值 3 + 5i 作为复数赋给变量 c。现在 c = 3 + 5i。使用简写声明 := 将 4 + 5i 赋给 d。加法操作 (c+d) 将复数相加,得到输出 7 + 10i。程序中给出的其他操作也以同样的方式工作。
输出
c's size is 16 bytes d's size is 16 bytes c's type is complex128 d's type is complex128 (7+10i) (-1+0i) (-13+35i) (0.902439024390244+0.12195121951219513i)
基本整数数据类型还有另外两种类型:Byte 和 Rune。Byte 和 Rune 是两种整数数据类型,分别可替代 uint8 和 int32 数据类型。
Byte: 字节数据类型表示 ASCII 字符。
Var name1 byte = 'B' // byte data type
例如,值为 'a' 的字节变量被转换为整数 97,值为 'b' 的字节变量被转换为整数 98,等等。
Rune:rune 数据类型表示以 UTF-8 格式编码的 Unicode 字符。例如:-在 Go 中,字符通过用单引号括起来表示,如:'c'。
var character = 'C ‘ // Type inferred as rune which is the default type for character values var r rune = ‘~’ // rune data type
例如:一个值为 Unicode 值 '~' 的 rune 变量 r 被转换为相应的 Unicode 码点 U+007E,其中 U+ 表示 Unicode,数字是十六进制,这本质上是一个整数。
注意
1. 在 Golang 中,没有 char 数据类型,而是使用 byte 和 rune 来表示 Golang 中的字符值。
2. 字符值的默认类型是 rune
字符串是 Golang 中另一种最常用的基本数据类型,它是一个字符序列,用于形成文本。一个数字、一个字母、一个符号,表示在双引号内。例如:考虑单词 Golang,在 Go 语言中,它通过表示在双引号内“Golang”来表示为字符串,一串数字 6456657,像 +_abcr 这样的符号在引号内形成字符串。
var text = “Golang”
var A = “6456657”
var B = “+_abcr”
package main
import ("fmt")
func main() {
/* var keyword assigns variable text with value “Golang” of string type */
var text string = "Golang"
/* short declaration to txt2 of string */
txt2 := "12345"
fmt.Printf("Type: %T, value: %v\n", text, text)
fmt.Printf("Type: %T, value: %v\n", txt2, txt2)
}
输出
Type : string, value : Golang Type : string, value : 12345
注意:引号内的任何内容都构成一个字符串。例如,txt2 被赋予了数字 12345,但它的类型是字符串而不是整数,因为它是在双引号内给出的
一个 boolean 数据类型使用 bool 关键字声明,有两种可能的推断,要么是 false 要么是 true。
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
//Default value will be false it not initialized
var v bool
fmt.Printf("a's value is %t\n", v)
//And operation on one true and other false
andOperation := 1 < 2 && 1 > 3
fmt.Printf("Ouput of AND operation on one true and other false %t\n", andOperation)
//OR operation on one true and other false
orOperation := 1 < 2 || 1 > 3
fmt.Printf("Ouput of OR operation on one true and other false: %t\n", orOperation)
//Negation Operation on a false value
negationOperation := !(1 > 2)
fmt.Printf("Ouput of NEGATION operation on false value: %t\n", negationOperation)
}
输出
v's value is false
Output of AND operation on one true and other false : false
Output of OR operation on one true and other false : true Output of NEGATION operation on false value : true
Golang 中的基本数据类型是
| 基本数据类型 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 整数 | 0,567,9,-8766 |
| float | 小数点数字 | 4.5,0.66,-67.98 |
| 字符串 | 字符序列 | “ Go Lang” “Learn e tutorial” |
| bool | True 或 False | true,false |
| 复数 | a+ib 形式的数字 | 5+4i,-7+76i |
| byte | 非负整数的字节。 | 115,2,97 |
| rune | 用于字符 | ‘>’, ‘8’, ‘i’ |
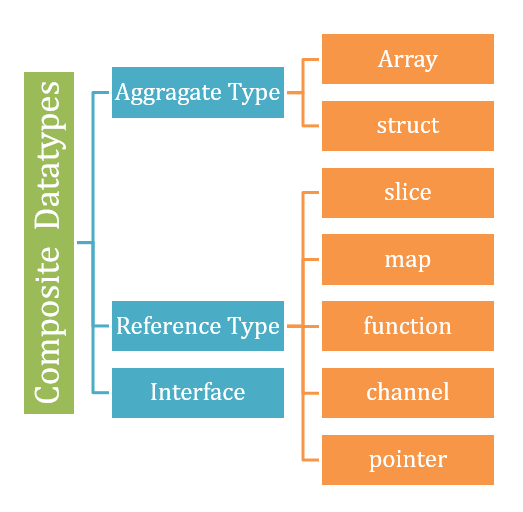
复合数据类型是程序员构建的任何数据类型,用于声明一个能够容纳一组值的单个变量,这需要借助 Go 编程语言的原始/基本数据类型,如 int、float、bool、string。
复合数据类型主要有三种