


在本教程中,您将学习 Golang 中方法的概念。方法和函数在用于常规事务时没有太大区别,但当函数进入一个称为类的概念时,它们就被称为方法。在本教程中,您将理解方法,以及是什么使它们与普通函数不同。
Go 编程语言不像其他面向对象的编程语言那样支持类和继承。Go 支持类型和方法,这使得 Golang 能够执行类似于面向对象编程语言的程序。
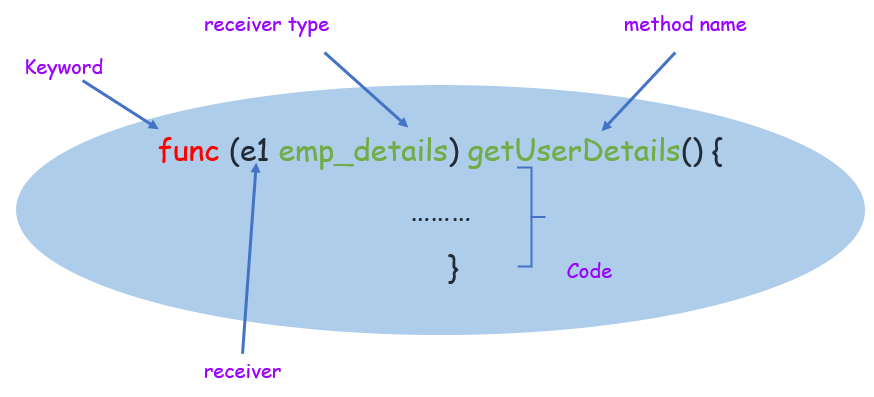
方法是一个带有特殊接收者参数的函数,接收者出现在它自己的参数列表中,形式为 (receiver receiver_type),位于 func 关键字和方法名称之间。接收者可以是结构体类型或非结构体类型。
在方法中,没有类的概念,但您可以使用 结构体 的概念。函数被引入一个结构体中,从而定义了一个方法。让我们来理解如何在 Go 程序中定义一个方法。
声明方法的语法
func (receiver receiver_type) method_name(arguments) return_type {
return_values
}
其中
让我们通过一个给定的程序来理解方法的概念。
该程序定义了一个名为 emp_details 的结构体类型,包含以下字段:Name、Age、Place、Id、salary,分别为字符串和整数数据类型。
// Defining a struct type
type emp_details struct {
Name string
Age int
Place string
Id int
salary int
定义的结构体类型 emp_details 有两个方法,分别是 getUserDetails() 和 getUserPlace()。
func (e1 emp_details) getUserDetails(){ //method 1
fmt.Println("Name of employee is : ",e1.Name )
fmt.Println("Age of employee is : ",e1.Age )
fmt.Println("ID of employee is : ",e1.Id )
}
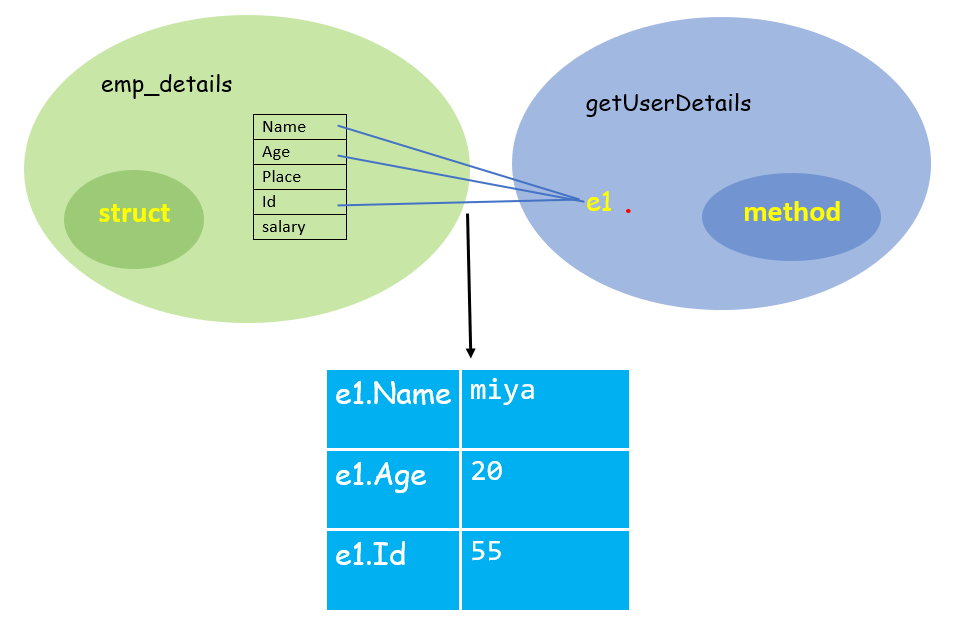
这是第一个名为 getUserDetails() 的方法,其接收者为 e1,接收者类型为 emp_details。在接收者声明中,emp_details 的实例被赋给变量 e1。花括号内包含某些打印语句,这些语句返回结构体类型 emp_details 中定义的字段的值。下图说明了该方法的运作方式。
让我们了解下一个使用的方法,即 getUserPlace()。
func (e1 emp_details) getUserPlace() string { //method 2
return e1.Place
}
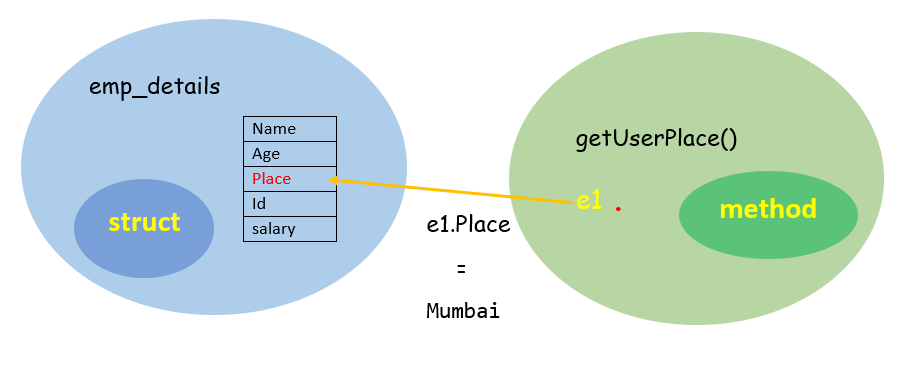
同样,接收者声明部分由 (e1 emp_details) 组成,其中 e1 是分配了 emp_details 实例的变量。该方法接收一个字符串类型的返回值。
注意: 您正在通过值将接收者 (e1 emp_details) 传递给 getUserPlace() 方法,这意味着在方法内部,您拥有所有 emp_details 的一个副本。
package main
import "fmt"
// Defining a struct type
type emp_details struct {
Name string
Age int
Place string
Id int
salary int
}
func (e1 emp_details) getUserDetails(){ //method
fmt.Println("Name of employee is : ",e1.Name )
fmt.Println("Age of employee is : ",e1.Age )
fmt.Println("ID of employee is : ",e1.Id )
}
func (e1 emp_details) getUserPlace() string { //method
return e1.Place
}
func main() {
//Declaring and Initializing variable of struct type
e1 := emp_details{"miya", 20,"Mumbai",0067,20000}
fmt.Println("Given employee details :",e1)
e1. getUserDetails()
fmt.Println("employee place is :",e1.getUserPlace())
}
输出
Given employee details : {miya 20 Mumbai 55 20000}
Name of employee is : miya
Age of employee is : 20
ID of employee is : 55
employee place is : Mumbai
type,那么它就是该类型的方法。一个附加到带有接收者的类型上的函数。这意味着如果您将一个函数附加到一个类型上,该函数就被称为接收者函数。接收者函数就是方法。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。下面的程序将让您了解什么是函数,什么是方法,以及它们有何不同。
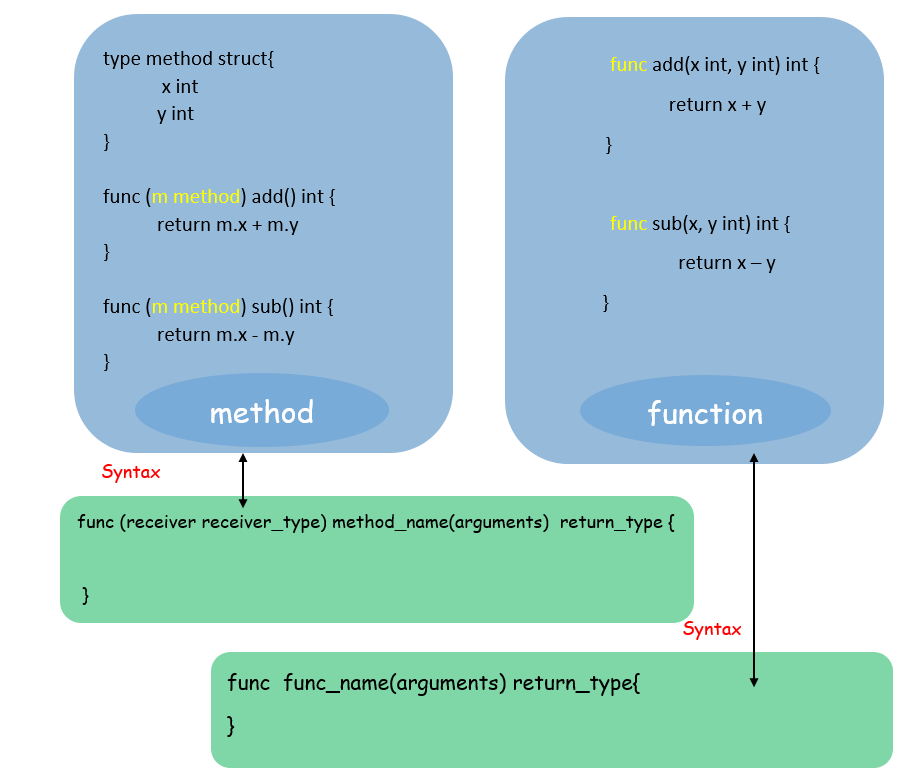
显示方法和函数差异的表格
| 方法 | 函数 |
|---|---|
|
方法有一个接收者参数,例如 (m method) (接收者 接收者类型) |
没有接收者参数 |
|
可以存在具有相同接收者名称的不同方法。 例如 func (m method) add() int func (m method) sub() int |
不能存在同名的不同函数 例如 func add(x int, y int) int func sub(x, y int) int |
| 方法使用结构体或非结构体类型的接收者。 | 函数没有接收者,所以没有这样的概念。 |
注意: 将表中的示例与上面的图片进行比较,以便更好地理解这个概念。
package main
import "fmt"
type method struct{
x int
y int
}
func (m method) add() int { //declaring method1
return m.x + m.y
}
func (m method) sub() int { //declaring method 2
return m.x - m.y
}
func add(x int, y int) int { //declaring a function function
return x + y
}
func sub(x, y int) int { //sub function of omit type
return x - y
}
func main() {
m := method{x:3,y:6} //intitializing
fmt.Println("The addition result using method is ", m.add()) //calling method 1
fmt.Println("The addition result using function ",add(10, 5)) //calling function add
fmt.Println("The subtraction result using method is ", m.sub()) //calling method 2
fmt.Println("The subtraction result using function is ",sub(10, 5)) // calling function sub
}
输出
The addition result using method is 9 The addition result using function 15 The subtraction result using method is -3 The subtraction result using function is 5
注意: 上面讨论的方法是结构体类型的。
Go 编程语言支持在结构体类型上定义方法。下面给出的程序定义了一个类型为 square 的结构体,使用关键字 struct,内部包含一个整数数据类型的属性 side。
接下来,定义了一个操作于 square 的方法。为了定义方法,使用关键字 func 后跟括号。在括号内,给出方法需要操作的对象,这里是 square。在方法内部,square 被引用为 s。方法的名称是 area(),返回类型为整数。area() 负责计算正方形的面积。
这里 s 通过方法传递,并使用点运算符访问属性 side。
在 main 函数内部,定义了对该方法的调用,为此我们定义了一个 square 的变量 s 并初始化其值。
package main
import ("fmt")
type square struct{ //defining a struct type
side int
}
func (s square ) area() int{ //area of square = side * side
return s.side* s.side
}
func main() {
s := square{side : 3} //Declaring and initializing a struct using a struct literal
fmt.Println("Area of square is : ",s.area(),"cm^2") // call to method area()
}
输出
Area of square is: 9 cm^2
注意: 该方法使用值类型接收者
func (s square ) area() int{
return s.side* s.side
}
与上述程序的主要区别在于传递一个指针,而不是值类型接收者。
在下面的程序中,main 函数定义了一个正方形 s 和一个指向该正方形的指针,并在打印函数中调用方法 s_ptr.perimeter(),该方法接受一个指针输入并打印出如下所示的输出。
package main
import ("fmt")
type square struct{ //defining a struct type
side int
}
func (s square ) area() int{ //area of square = side * side
return s.side* s.side
}
func (s *square) perimeter() int { //pointer to the struct type square
return 4 * s.side
}
func main() {
s := square{side : 3} //Declaring and initializing a struct using a struct literal
fmt.Println("Area of square is : ",s.area(),"cm^2")
s_ptr := &s //define a pointer
fmt.Println("The perimeter of a square is 4 * sides :", s_ptr.perimeter())
}
输出
Area of square is : 9 cm^2 The perimeter of a square is 4 * sides : 12