


在本教程中,我们将介绍 Go 的 struct 数据类型,它属于复合类型的聚合数据类型。在本教程中,您将了解 Go 中结构体的确切含义、Go 中的定义和声明语法、命名结构体、访问和嵌套结构体数据类型等。
结构体是由一组字段组成的结构,每个字段存储不同类型的数据。因此,在 Golang 中,结构体被归类为复合数据类型的聚合类型。结构体中定义的字段具有不同的属性,并且每个属性都具有指定的类型和分配的值。
例如:考虑一个组织的员工数据库,它保存所有员工的相关记录,例如员工的姓名、年龄、ID、地点、薪水等。这些是不同的字段,包含各种类型的数据,它们在结构体数据类型下指向单个实体。
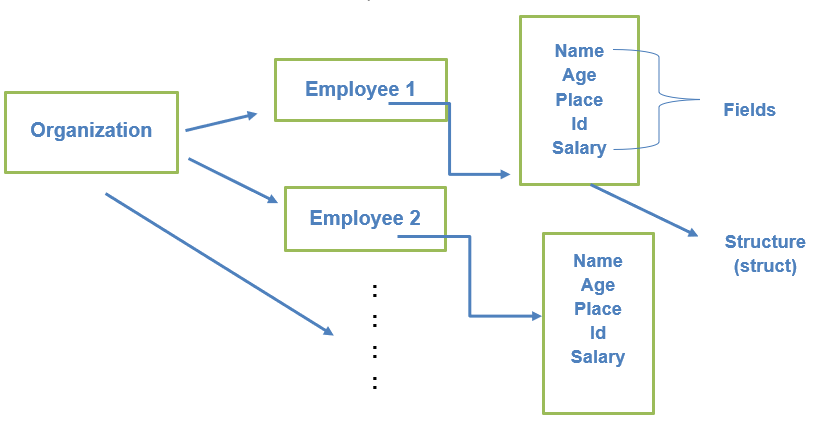
定义结构体需要两个关键字。它们是
type emp_details struct{
Name string
Age int
Place string
Id int
Salary int
}
上面的代码显示了一个名为 emp_details 的结构体,其中包含姓名、年龄、地点、ID 和薪水 字段。上面的结构体定义是一个 命名结构体,因为它创建了一个名为 emp_details 的新结构体数据类型。
type 关键字表示一个新类型,struct 关键字将该类型定义为结构体。 type 关键字后面跟着结构体的名称(emp_details)。 string 类型,薪水是 int 类型,依此类推。每个字段写在一行上,可以通过将具有相似数据类型的字段分组到一行上来改变,如下所示
type emp_details struct{
Name Place string //single line declaration of same type(string)
Age Id Salary Int //single line declaration of same type(integer)
}
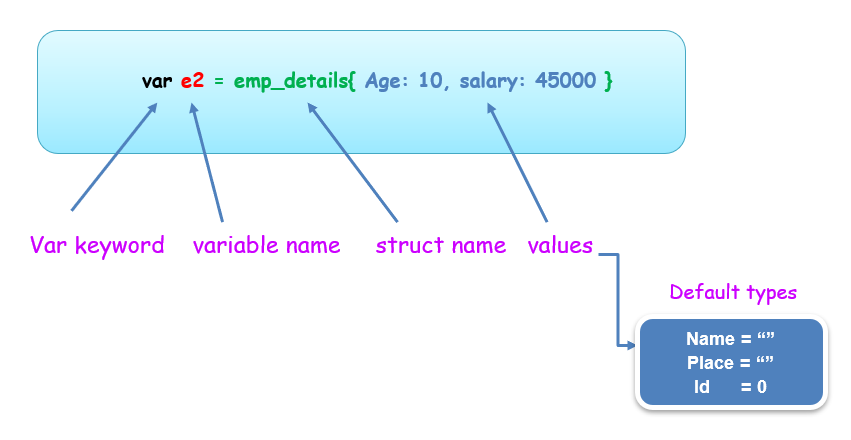
在 Go 语言中,结构体通过使用 var 关键字或使用符号“:=”的简短声明来初始化。每当结构体字段未初始化为任何特定值时,它们将被设置为默认类型。
让我们通过示例逐一理解
// Golang program to show how to declare and define the struct
package main
import "fmt"
// Defining a struct type
type emp_details struct {
Name string
Age int
Place string
Id int
salary int
}
func main() {
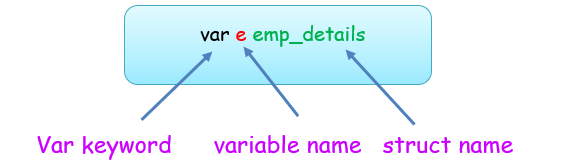
// Declaring a variable e `struct` type using var keyword
var e emp_details
fmt.Println(e)
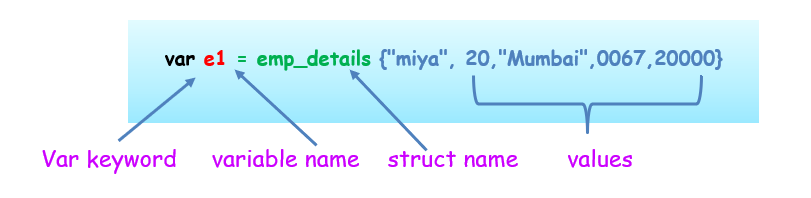
//Declaring and Initializing variable of struct type
var e1 = emp_details{"miya", 20,"Mumbai",0067,20000}
fmt.Println(e1)
//Declaring and Initializing variable of struct type
var e2 = emp_details{Age: 10, salary: 45000}
fmt.Println(e2)
}
输出
{ 0 0 0}
{miya 20 Mumbai 55 20000}
{ 10 0 45000}
解释
// Golang program to show how to declare and define the struct
package main
import "fmt"
// Defining a struct type
type emp_details struct {
Name string
Age int
Place string
Id int
salary int
}
func main() {
// Shorthand notation Declaration and Initialization
e1 := emp_details{"miya", 20,"Mumbai",0067,20000}
fmt.Println(e1)
//Shorthand notation Declaration and Initialization
e2 := emp_details{Age: 10, salary: 45000}
fmt.Println(e2)
}
输出
{miya 20 Mumbai 55 20000}
{ 10 0 45000}
解释

// Golang program to show how to declare and define the struct
package main
import "fmt"
// Defining a struct type
type emp_details struct {
Name string
Age int
Place string
Id int
salary int
}
func main() {
// Declaring a variable of a `struct` type
// All the struct fields are initialized with their zero value
var e emp_details
fmt.Println(e)
}
输出
{ 0 0 0}
解释
在 Golang 中,结构体字段通过点 (.) 运算符进行访问。使用点运算符可以轻松获取和设置 Golang 中的结构体字段。
在下面给出的程序中,创建了一个名为 emp_details 的结构体,它有 5 个字段。要访问并为字符串类型的 Name 字段赋值,我们使用以下语法
让我们通过示例来理解
// Golang program to show how to declare and define the struct
package main
import "fmt"
// Defining a struct type
type emp_details struct {
Name string
Age int
Place string
Id int
salary int
}
func main() {
// Declaring a variable of a `struct` type
// All the struct fields are initialized with their zero value
var e emp_details
//setting values using dot(.) operator
e.Name = "Nainika"
e.Age=5
e.Place = "MALAYSIA"
e.Id = 007
e.salary = 100000
//Displays output
输出
e.Name : Nainika e.Age : 5 e.Place : MALAYSIA e.Id: 7 e.salary : 100000
在 Golang 结构体数据类型中,提供了一个名为嵌入的属性,它允许将一个结构体嵌入到另一个结构体中。结构体类型可以定义为另一个结构体类型。
语法
type Address struct {
City string
Country string
}
type emp_details struct {
Name string
Age int
Address
}
package main
import "fmt"
type Address struct {
city string
country string
}
type emp_details struct {
name string
age int
Address
}
func main() {
emp := emp_details{
name: "Joseph",
age: 54,
Address: Address{
city: "italy",
country: "USA",
},
}
fmt.Println("Name of employee:", emp.name)
fmt.Println("Age:", emp.age)
fmt.Println("City:", emp.city)
fmt.Println("Country:", emp.country)
}
输出
Name of employee: Joseph Age: 54 City: italy Country: USA
结构体数据类型的指针使用“&”运算符创建。所有变量都有内存位置,指针与 & 运算符一起用于访问变量操作数被分配到的内存位置,而 * 运算符用于访问该位置中保存的相应值。
示例:
package main
import "fmt"
// declaration of struct type
type emp_details struct {
Age int
Name string
Salary int
}
func main() {
var emp1 = &emp_details{40, "zen", 45000} // all values are shown
fmt.Println(emp1)
var emp2 = &emp_details{}
emp2.Age = 10
emp2.Name = "Vihan"
fmt.Println(emp2) // salary not mentioned
}
输出
&{40 zen 45000}
&{10 Vihan 0}
解释

var emp2 = &emp;_details{}
emp2.Age = 10
emp2.Name = "Vihan"