


在所有编程语言中,数据类型定义了要存储在计算机内存中的数据类型。数据是存储在变量(链接到变量)中的值。因此,您可以将数据类型定义为表示数据类型的分类,例如数字(8)、字符串(“hello”)、浮点数(8.34)、复数(4+3i)等。让我们来学习 R 编程语言中的基本数据类型。
除了数据类型,我们还会讨论 R 中使用的数据结构类型。您现在可能对数据类型和数据结构这两个术语感到困惑。数据类型用于为变量赋单个值,而数据结构则保存由数据类型组成的数据或值的集合。让我们来了解它们在 R 中的真正含义。
数据类型用于表示程序中使用的数据类型,或变量将保存的数据类型。它是与数据关联的属性,用于指定其类型,进而在程序执行期间告诉编译器如何解释该值。
在 R 中,变量不会声明为任何特定的数据类型,而是变量本身获取分配给它的数据的类型。
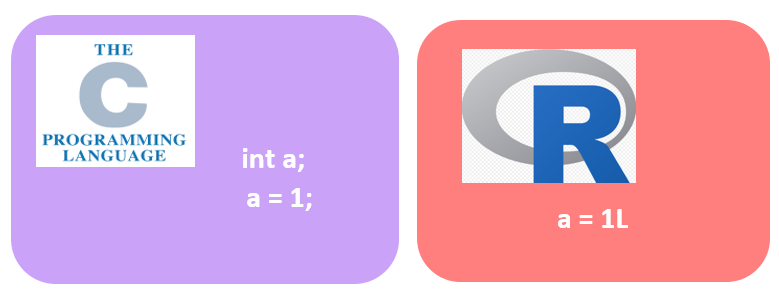
看图可以发现,在 C 语言中变量 **a** 先被声明为 **整数数据类型(int)**,然后被赋值为 **1**。而在 R 中,变量 **'a'** 的初始化及其数据类型(**整数数据类型**)的声明在一行中完成。因此,在 R 编程语言中,变量本身会根据分配给它的值来声明其数据类型。
注意:在 R 中,变量获取分配给它的对象(数据)的数据类型
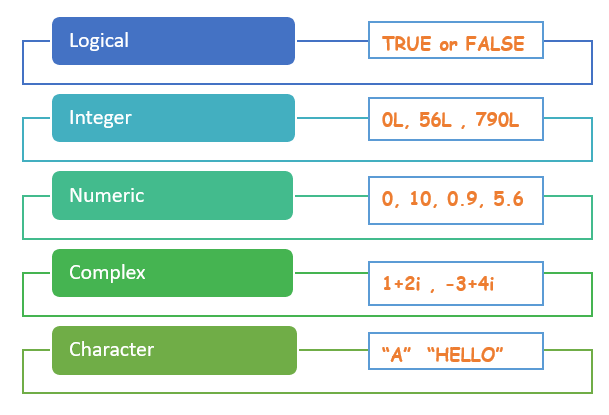
以下是 R 编程语言中的五种基本数据类型。
在 R 编程语言中,逻辑数据类型拥有(包含)两个可能的值:`TRUE` 或 `FALSE`。
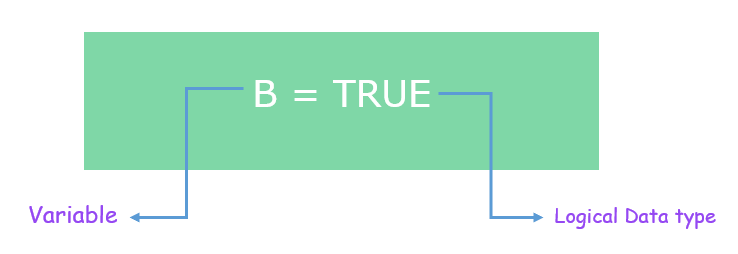
当程序员在程序执行期间将值 **TRUE** 分配给 变量 **B** 时,编译器将其解释为 **逻辑数据类型**。换句话说,**变量 B** 所包含的数据类型是 **逻辑**。因此,与 **B** 关联的属性是逻辑类型。
# R program to show logical data type
# Assigns values
A = TRUE
B = FALSE
C = 1
D = 8
# Comparing two values (1>8) using logical operator > returns logical values
E = C > D
# print the values
print(A)
print(B)
print(C)
print(D)
print(E)
# print the class name of z
print(class(A))
print(class(B))
print(class(E))
# print the type of z
print(typeof(A))
print(typeof(B))
print(typeof(C))
输出
[1] TRUE [1] FALSE [1] 1 [1] 8 [1] FALSE [1] "logical" [1] "logical" [1] "logical" [1] "logical" [1] "logical" [1] "logical"
在 R 编程语言中,数值数据类型支持小数(4.5, 0.001)和非小数(1, 4, 78, 95678)值。
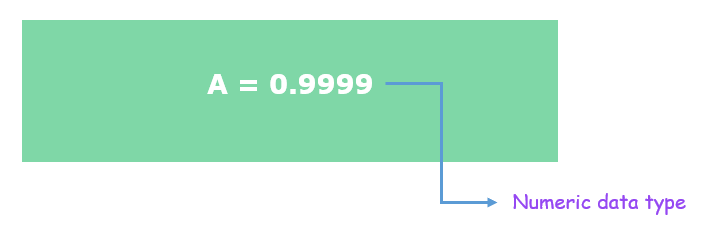
变量 A 被分配了数值数据类型的 0.9999 值。
# R program to show numeric data type
# variables A ,B Assigned with values 1.11 & 8
A = 1.11
B = 8
# print the values of A & B
print(A)
print(B)
# print the class name of A & B
print(class(A))
print(class(B))
# print the type of A & B
print(typeof(A))
print(typeof(B))
输出
[1] TRUE [1] FALSE [1] 1 [1] 8 [1] FALSE [1] "logical" [1] "logical" [1] "logical" [1] "logical" [1] "logical" [1] "logical"
R 编程语言支持存储整数值。通过在值后面附加“L”来定义一个值是整数值。
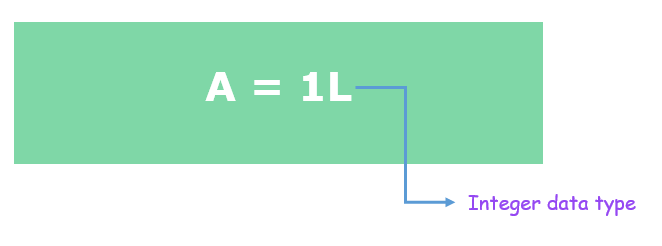
# R program to show integer data type
# variables A Assigned with values 1L
A = 1L
# print the values
print(A)
# print the class name
print(class(A))
# print the type
print(typeof(A))
输出
[1] 1 [1] "integer" [1] "integer"
变量 A 以整数数据类型存储,值为 1。带“L”的十进制值不能附加“L”,否则会产生警告消息,如下面的输出所示。
# A R program to show error in integer data type
# variables A Assigned with values 1L
A = 1L
B = 1.56L
# print the values
print(A)
print(B)
输出
[1] 1
[1] 1.56
Warning message:
In source("C:/Users/Desktop/R/R Pgms/4_Tutorial_numeric type.R") :
integer literal 1.56L contains decimal; using numeric value
输出表明 1.56 是数值数据类型,因为它是一个小数而不是整数。
注意:在 R 中,当值附加“L”作为其后缀时,表示它是整数数据类型。
R 支持复数,即具有实部和虚部的数字。复数数据类型用于在 R 中指定复数。
# A R program to show complex data type
# variables A Assigned with values -3+4i
A = -3+4i
# print the values
print(A)
# print the class name
print(class(A))
输出
[1] -3+4i [1] "complex"
R 支持存储字符串值,例如字母序列或单个字母、数字、特殊符号。为了让编译器理解它是字符数据类型,您需要将它们放在单引号(‘ ’)或双引号(“ ”)内。
# A R program to show character data type
# variables Assigned with values
Lang = "Learn eTutorials"
Year = "2022"
Tutorial ='4.0'
# print the values
print(Lang )
print(Year )
print(Tutorial )
# print the class name
print(class(Lang))
print(class(Year))
print(class(Tutorial))
输出
[1] "Learn eTutorials" [1] "2022" [1] "4.0" [1] "character" [1] "character" [1] "character"
注意:除了这些基本数据类型外,还有一种称为“原始”的数据类型。
原始数据类型包含字节值。
#Raw Data type
A <- charToRaw("Learn eTutorials")
cat(A,"\n")
cat("The data type of A is ",class(A),"\n\n")
输出
4c 65 61 72 6e 20 65 54 75 74 6f 72 69 61 6c 73 The data type of A is raw
| 基本数据类型 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 逻辑型 | 仅包含 TRUE 或 FALSE 值。 | TRUE 或 FALSE |
| 整型 | 包含整数值(正整数和 0)。 | 0L, 56L, 7990L |
| 数值型 | 同时包含整数和十进制值。 | 0, 10, 0.009, 5.6 |
| 复数型 | 包含实部和虚部的值。 | 1+2i , -3+4i |
| 字符 | 包含单个字符或单词序列 | “A”, “HELLO” |
| 原始 | 原始数据类型包含字节值。 | 4c 65 61 72 6e 20 65 54 75 74 6f 72 69 61 6c 73 |
# A simple program to show all basic data types in R
# Assign value to variables
A = 0.9999 # Numeric data type
B = TRUE # logical data type
C= 6L #integer data type
D="HELLO" #character date type
E = 1+2i #complex data type
# print the class name of variable
cat("The data type of A is ",class(A),"\n")
cat("The data type of B is ",class(B), "\n")
cat("The data type of C is ",class(C),"\n")
cat("The data type of D is ",class(D),"\n")
cat("The data type of E is ",class(E),"\n")
输出
The data type of A is numeric The data type of B is logical The data type of C is integer The data type of D is character The data type of E is complex
上面程序中使用了一些 R 内置函数 class() 和 typeof(),它们可以帮助程序员(用户)识别相应变量或数据的特征。
整数不能存储带有小数点的数值。要在 R 中存储小数点值,可以使用数值数据类型。要将一个值指定为整数类型,请在每个值末尾附加“L”。
以下示例使用了向量数据结构,它包含一个或多个相同数据类型元素。它表示为 c(),括号内包含具有相同数据类型的值。
| 整数数据类型 | 数值数据类型 |
|---|---|
|
|
|
示例 1:
输出 [1] "integer" [1] 0 3666 1000000 |
示例 2:
输出 [1] "numeric" [1] 5.000 45.000 1.689 示例 3:
输出 [1] "numeric" 0 3666 1000000 |